The Effect of an Abdominal Binder on Postoperative Pain After Laparoscopic Incisional Hernia Repair–A Multicenter, Randomized Pilot Trial (ABIHR-I) of the Intraperitoneal Onlay-Mesh Technique
- PMID: 34857076
- PMCID: PMC8704821
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.m2021.0250
The Effect of an Abdominal Binder on Postoperative Pain After Laparoscopic Incisional Hernia Repair–A Multicenter, Randomized Pilot Trial (ABIHR-I) of the Intraperitoneal Onlay-Mesh Technique
Abstract
Background: Incisional hernias with apertures measuring less than 7 cm can generally be treated adequately with the laparoscopic intraperitoneal onlay-mesh (IPOM) technique. The wearing of an abdominal binder after surgery is often recommended in order to promote wound healing and prevent recurrent herniation. We carried out a multicenter, randomized pilot trial to evaluate the utility of abdominal binders.
Methods: The trial was conducted from May 2019 to December 2020. Persons with a laparoscopic IPOM procedure for treatment of an incisional hernia were included in the trial and randomized preoperatively (1:1). The patients in the abdominal binder group wore an abdominal binder during the day for 14 days after surgery, while those in the control group wore no binder. The primary endpoint was pain at rest on postoperative days 1, 2, and 14, as measured on a visual analog scale. The secondary endpoints were overall subjective well-being, the rates of wound infection, recurrence, and complications, mobility, and the rate and size of postoperative seromas (on postoperative days 1, 2, and 14).
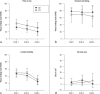
Results: Forty patients were included. Three were excluded because of conversion to an open surgical technique. The biometric and perioperative data of the abdominal binder group (n = 18) and the control group (n = 19) did not differ to any statistically significant extent. The patients in the binder group had significantly less postoperative pain (F [dfn, dfd]) 4.44, 95% confidence interval [1; 35]; p = 0.042).The patients in the binder group also had better overall subjective well-being and a higher rate of postoperative seroma formation, but these differences did not reach statistical significance. There was less limitation of mobility than in the control group; however, this difference also did not attain statistical significance.
Conclusion: An abdominal binder may reduce pain after incisional hernia repair with the IPOM technique. The postoperative use of analgesic medication was not measured.
Figures
References
-
- Hoer J, Lawong G, Klinge U, Schumpelick V. [Factors influencing the development of incisional hernia. A retrospective study of 2,983 laparotomy patients over a period of 10 years] Chirurg. 2002;73:474–480. - PubMed
-
- Schwarz J, Reinpold W, Bittner R. Endoscopic mini/less open sublay technique (EMILOS)-a new technique for ventral hernia repair. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2017;402:173–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources