Regulation of the EphA2 receptor intracellular region by phosphomimetic negative charges in the kinase-SAM linker
- PMID: 34857764
- PMCID: PMC8639986
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-27343-z
Regulation of the EphA2 receptor intracellular region by phosphomimetic negative charges in the kinase-SAM linker
Abstract
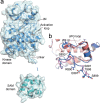
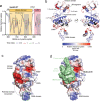
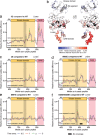
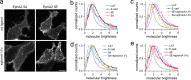
Eph receptor tyrosine kinases play a key role in cell-cell communication. Lack of structural information on the entire multi-domain intracellular region of any Eph receptor has hindered understanding of their signaling mechanisms. Here, we use integrative structural biology to investigate the structure and dynamics of the EphA2 intracellular region. EphA2 promotes cancer malignancy through a poorly understood non-canonical form of signaling involving serine/threonine phosphorylation of the linker connecting its kinase and SAM domains. We show that accumulation of multiple linker negative charges, mimicking phosphorylation, induces cooperative changes in the EphA2 intracellular region from more closed to more extended conformations and perturbs the EphA2 juxtamembrane segment and kinase domain. In cells, linker negative charges promote EphA2 oligomerization. We also identify multiple kinases catalyzing linker phosphorylation. Our findings suggest multiple effects of linker phosphorylation on EphA2 signaling and imply that coordination of different kinases is necessary to promote EphA2 non-canonical signaling.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Protein kinase C phosphorylates the EphA2 receptor on serine 892 in the regulatory linker connecting the kinase and SAM domains.Cell Signal. 2020 Sep;73:109668. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109668. Epub 2020 May 13. Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 32413552 Free PMC article.
-
The SAM domain inhibits EphA2 interactions in the plasma membrane.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017 Jan;1864(1):31-38. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.10.011. Epub 2016 Oct 21. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 27776928 Free PMC article.
-
PIP2 promotes conformation-specific dimerization of the EphA2 membrane region.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100149. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.016423. Epub 2020 Dec 10. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33277361 Free PMC article.
-
The Sam Domain of EphA2 Receptor and its Relevance to Cancer: A Novel Challenge for Drug Discovery?Curr Med Chem. 2016;23(42):4718-4734. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666161101100722. Curr Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27804871 Review.
-
Cataract-related mutations in EphA2: a survey of literature data and the relevance of the receptor Sam domain.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2025 Apr-May;29(4-5):239-265. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2025.2500422. Epub 2025 May 12. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2025. PMID: 40310271 Review.
Cited by
-
EPHA2 Receptor as a Possible Therapeutic Target in Viral Infections.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(35):5670-5701. doi: 10.2174/0109298673256638231003111234. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37828671 Review.
-
Optimization of the Lead Compound NVP-BHG712 as a Colorectal Cancer Inhibitor.Chemistry. 2023 Apr 21;29(23):e202203967. doi: 10.1002/chem.202203967. Epub 2023 Mar 22. Chemistry. 2023. PMID: 36799129 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting EPHA2 with Kinase Inhibitors in Colorectal Cancer.ChemMedChem. 2023 Dec 1;18(23):e202300420. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202300420. Epub 2023 Oct 5. ChemMedChem. 2023. PMID: 37736700 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol-dependent dimerization and conformational dynamics of EphA2 receptors from coarse-grained and all-atom simulations.Structure. 2025 Jul 3;33(7):1275-1287.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2025.03.014. Epub 2025 Apr 24. Structure. 2025. PMID: 40280119
-
Engineering of an EPHA2-Targeted Monobody for the Detection of Colorectal Cancer.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2024 May-Jun;21(3):285-294. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20447. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 38670584 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

