Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies
- PMID: 34857780
- PMCID: PMC10425161
- DOI: 10.1038/s41572-021-00325-7
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies
Abstract
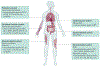
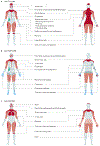
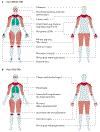
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM), also known as myositis, are a heterogeneous group of autoimmune disorders with varying clinical manifestations, treatment responses and prognoses. Muscle weakness is usually the classical clinical manifestation but other organs can be affected, including the skin, joints, lungs, heart and gastrointestinal tract, and they can even result in the predominant manifestations, supporting that these are systemic inflammatory disorders. Different myositis-specific autoantibodies have been identified and, on the basis of clinical, histopathological and serological features, IIMs can be classified into several subgroups — dermatomyositis (including amyopathic dermatomyositis), antisynthetase syndrome, immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy, inclusion body myositis, polymyositis and overlap myositis. The prognoses, treatment responses and organ manifestations vary among these groups, implicating different pathophysiological mechanisms in each subtype. A deeper understanding of the molecular pathways underlying the pathogenesis and identifying the autoantigens of the immune reactions in these subgroups is crucial to improve outcomes. New, more homogeneous subgroups defined by autoantibodies may help define disease mechanisms, and will also be important in future clinical trials to develop targeted therapies and in identifying biomarkers to guide treatment decisions for the individual patient.
Conflict of interest statement
I.E.L. has received research funding from Astra Zeneca and Bristol Myers Squibb and has served on advisory boards for Corbus Pharmaceutical, EMD Serono Research & Development Institute, Argenx, Octapharma, Kezaar, Orphazyme, Janssen and Pfizer, and has stock shares in Roche and Novartis.
M.F. has received research funding and speakers fee from Abbvie, Amgen, Eli-Lilly, Japan Blood Product Organization, Kyowa-Kirin, Maruho, Novartis, Sanofi and Taiho.
J.V. has been on Speakers Bureaus of Abbvie, Biogen, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi and UCB, and has consulted for Abbvie, Argenx, Boehringer, Eli Lilly and Octapharma.
R.A. receives research funding from BMS, Mallinckrodt, Genentech and Pfizer, and has served as consultant for BMS, Mallinckrodt, Pfizer, Orphazyme, Octapharma, Kyverna, Kezar, Janssen, Csl Behring, Corbus, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Argenx, Alexion, Q32 and Abbvie.
L.C-S. has research support from Pfizer, Corbus and Kezar, and has served on advisory boards for UCB (not myositis related), Janssen, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Mallinckrodt, Serono, Argenx, Roivant and Dysimmune Disease Foundation (DDF), and received compensation for consultancy work from Guidepoint and Allogene. She is also a patent holder on an assay for anti-HMGCR autoantibodies for which she received royalty payments from Inova Diagnostics.
A.L.M is a patent holder on an assay for anti-HMGCR autoantibodies, but does not receive any royalties.
All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

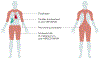



References
-
- McHugh NJ & Tansley SL Autoantibodies in myositis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 14, 290–302 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Walton JN Some Diseases of Muscle. Lancet 1, 447–452 (1964). - PubMed
-
- Hoogendijk JE, et al. 119th ENMC international workshop: trial design in adult idiopathic inflammatory myopathies, with the exception of inclusion body myositis, 10–12 October 2003, Naarden, The Netherlands. Neuromuscul Disord 14, 337–345 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Loarce-Martos J, Lilleker JB, Parker M, McHugh N & Chinoy H Polymyositis: is there anything left? A retrospective diagnostic review from a tertiary myositis centre. Rheumatology (Oxford) 60, 3398–3403 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

