KSHV transactivator-derived small peptide traps coactivators to attenuate MYC and inhibits leukemia and lymphoma cell growth
- PMID: 34857874
- PMCID: PMC8639922
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-021-02853-0
KSHV transactivator-derived small peptide traps coactivators to attenuate MYC and inhibits leukemia and lymphoma cell growth
Abstract
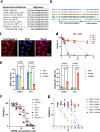
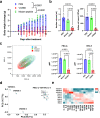
In herpesvirus replicating cells, host cell gene transcription is frequently down-regulated because important transcriptional apparatuses are appropriated by viral transcription factors. Here, we show a small peptide derived from the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus transactivator (K-Rta) sequence, which attenuates cellular MYC expression, reduces cell proliferation, and selectively kills cancer cell lines in both tissue culture and a xenograft tumor mouse model. Mechanistically, the peptide functions as a decoy to block the recruitment of coactivator complexes consisting of Nuclear receptor coactivator 2 (NCOA2), p300, and SWI/SNF proteins to the MYC promoter in primary effusion lymphoma cells. Thiol(SH)-linked alkylation for the metabolic sequencing of RNA (SLAM seq) with target-transcriptional analyses further confirm that the viral peptide directly attenuates MYC and MYC-target gene expression. This study thus provides a unique tool to control MYC activation, which may be used as a therapeutic payload to treat MYC-dependent diseases such as cancers and autoimmune diseases.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing interests: M.S. and Y.I. filed PCT Patent Application No. PCT/US2021/055979 through University of California Davis, and are founders of VGN Bio, Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Myc is required for the maintenance of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency.J Virol. 2010 Sep;84(17):8945-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00244-10. Epub 2010 Jun 23. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20573831 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Novel Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Orf50 Transcripts: Discovery of New RTA Isoforms with Variable Transactivation Potential.J Virol. 2016 Dec 16;91(1):e01434-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01434-16. Print 2017 Jan 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27795414 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency-associated nuclear antigen by the lytic transactivator RTA: a novel mechanism for establishment of latency.J Virol. 2005 Jun;79(12):7453-65. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.12.7453-7465.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15919901 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclooxygenase-2-prostaglandin E2-eicosanoid receptor inflammatory axis: a key player in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpes virus associated malignancies.Transl Res. 2013 Aug;162(2):77-92. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2013.03.004. Epub 2013 Apr 6. Transl Res. 2013. PMID: 23567332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathological Features of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Infection.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1045:357-376. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-7230-7_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29896675 Review.
Cited by
-
KSHV Topologically Associating Domains in Latent and Reactivated Viral Chromatin.J Virol. 2022 Jul 27;96(14):e0056522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00565-22. Epub 2022 Jul 11. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35867573 Free PMC article.
-
KSHV RTA utilizes the host E3 ubiquitin ligase complex RNF20/40 to drive lytic reactivation.J Virol. 2023 Nov 30;97(11):e0138923. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01389-23. Epub 2023 Oct 27. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37888983 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus terminal repeat regulates inducible lytic gene promoters.J Virol. 2024 Feb 20;98(2):e0138623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01386-23. Epub 2024 Jan 19. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38240593 Free PMC article.
-
The recent progress of peptide regulators for the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 16;10:1164656. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1164656. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37396899 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tsafou K, Tiwari PB, Forman-Kay JD, Metallo SJ, Toretsky JA. Targeting intrinsically disordered transcription factors: changing the paradigm. J. Mol. Biol. 2018;430:2321–2341. - PubMed
-
- Soucek L, et al. Design and properties of a Myc derivative that efficiently homodimerizes. Oncogene. 1998;17:2463–2472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

