Nuclear deformation guides chromatin reorganization in cardiac development and disease
- PMID: 34857921
- PMCID: PMC9300284
- DOI: 10.1038/s41551-021-00823-9
Nuclear deformation guides chromatin reorganization in cardiac development and disease
Abstract
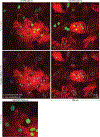
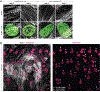
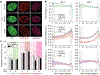
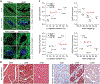
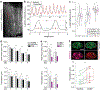
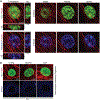
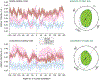
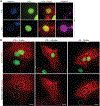
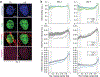
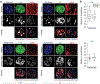
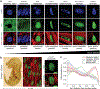
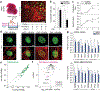
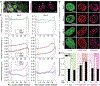
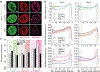
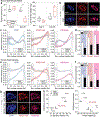
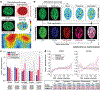
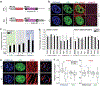
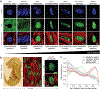
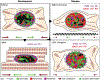
In cardiovascular tissues, changes in the mechanical properties of the extracellular matrix are associated with cellular de-differentiation and with subsequent functional declines. However, the underlying mechanoreceptive mechanisms are largely unclear. Here, by generating high-resolution, full-field strain maps of cardiomyocyte nuclei during contraction in vitro, complemented with evidence from tissues from patients with cardiomyopathy and from mice with reduced cardiac performance, we show that cardiomyocytes establish a distinct nuclear organization during maturation, characterized by the reorganization of H3K9me3-marked chromatin towards the nuclear border. Specifically, we show that intranuclear tension is spatially correlated with H3K9me3-marked chromatin, that reductions in nuclear deformation (through environmental stiffening or through the disruption of complexes of the linker of nucleoskeleton and cytoskeleton) abrogate chromatin reorganization and lead to the dissociation of H3K9me3-marked chromatin from the nuclear periphery, and that the suppression of H3K9 methylation induces chromatin reorganization and reduces the expression of cardiac developmental genes. Overall, our findings indicate that, by integrating environmental mechanical cues, the nuclei of cardiomyocytes guide and stabilize the fate of cells through the reorganization of epigenetically marked chromatin.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Engler AJ, Sen S, Sweeney HL & Discher DE Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell 126, 677–89 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Lampi MC & Reinhart-King CA Targeting extracellular matrix stiffness to attenuate disease: From molecular mechanisms to clinical trials. Sci. Transl. Med 10, eaao0475 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

