A Prognostic Model Incorporating Red Cell Distribution Width to Platelet Ratio for Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury
- PMID: 34858027
- PMCID: PMC8631984
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S337040
A Prognostic Model Incorporating Red Cell Distribution Width to Platelet Ratio for Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury
Abstract
Background: As an inflammation-based marker, red cell distribution width to platelet ratio (RPR) has been verified to be associated with disease severity and outcome in many clinical settings. We designed this study to evaluate the prognostic value of RPR in patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI).
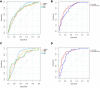
Methods: A total of 420 patients admitted with TBI were included in this study. Laboratory and clinical data were collected from an electronic medical record system. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were sequentially performed to discover risk factors of in-hospital mortality. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were drawn to confirm the predictive value of different markers including RPR in training set and testing set.
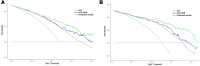
Results: Non-survivors had higher level of RPR than survivors (P<0.001). Logistic regression analysis showed that RPR was significantly associated with mortality even after adjusting for confounding factors (P<0.001). The area under the ROC curve (AUC) value of Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) for predicting mortality was 0.761 and 0775 in training set and testing set, respectively. And the constructed predictive model incorporating RPR had the highest AUC value of 0.858 and 0.884 in training set and testing set.
Conclusion: RPR is significantly associated with mortality in TBI patients. Utilizing RPR to construct a predictive model is valuable to evaluate prognosis of TBI patients.
Keywords: marker; prognosis; red cell distribution to platelet ratio; traumatic brain injury.
© 2021 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Red Cell Distribution Width to Platelet Count Ratio: A Promising Routinely Available Indicator of Mortality for Acute Traumatic Brain Injury.J Neurotrauma. 2022 Jan;39(1-2):159-171. doi: 10.1089/neu.2020.7481. Epub 2021 May 3. J Neurotrauma. 2022. PMID: 33719580
-
Red cell distribution width to platelet ratio: new and promising prognostic marker in acute pancreatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Oct 21;20(39):14450-4. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14450. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25339831 Free PMC article.
-
Liver fibrosis score is associated with the mortality of traumatic brain injury patients.Neurosurg Rev. 2023 Aug 15;46(1):201. doi: 10.1007/s10143-023-02095-0. Neurosurg Rev. 2023. PMID: 37581745
-
A Prediction Model for In-Hospital Mortality of Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients Based on Red Cell Distribution Width-to-Platelet Ratio.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023 Sep 20;18:2079-2091. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S418162. eCollection 2023. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023. PMID: 37750166 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of red blood cell distribution width to platelet ratio for predicting staging liver fibrosis in chronic liver disease patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Apr;98(14):e15096. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015096. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30946368 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Novel Blood Inflammatory Indicator for Predicting Deterioration Risk of Mild Traumatic Brain Injury.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Apr 26;14:878484. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.878484. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35557838 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting mortality in patients with acute severe traumatic brain injury: A retrospective analysis.Neurol Sci. 2024 Oct;45(10):4931-4956. doi: 10.1007/s10072-024-07572-y. Epub 2024 May 9. Neurol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38722502
-
A Meta-analysis of Predicting Disorders of Consciousness After Traumatic Brain Injury by Machine Learning Models.Alpha Psychiatry. 2024 Jun 1;25(3):290-303. doi: 10.5152/alphapsychiatry.2024.231443. eCollection 2024 Jun. Alpha Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39148604 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Mortality in Geriatric Traumatic Brain Injury Patients Using Machine Learning Algorithms.Brain Sci. 2023 Jan 3;13(1):94. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13010094. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 36672075 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

