Higher-Order Conditioning With Simultaneous and Backward Conditioned Stimulus: Implications for Models of Pavlovian Conditioning
- PMID: 34858147
- PMCID: PMC8632485
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2021.749517
Higher-Order Conditioning With Simultaneous and Backward Conditioned Stimulus: Implications for Models of Pavlovian Conditioning
Abstract
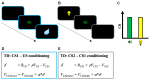
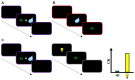
In a new environment, humans and animals can detect and learn that cues predict meaningful outcomes, and use this information to adapt their responses. This process is termed Pavlovian conditioning. Pavlovian conditioning is also observed for stimuli that predict outcome-associated cues; a second type of conditioning is termed higher-order Pavlovian conditioning. In this review, we will focus on higher-order conditioning studies with simultaneous and backward conditioned stimuli. We will examine how the results from these experiments pose a challenge to models of Pavlovian conditioning like the Temporal Difference (TD) models, in which learning is mainly driven by reward prediction errors. Contrasting with this view, the results suggest that humans and animals can form complex representations of the (temporal) structure of the task, and use this information to guide behavior, which seems consistent with model-based reinforcement learning. Future investigations involving these procedures could result in important new insights on the mechanisms that underlie Pavlovian conditioning.
Keywords: backward conditioning; higher-order conditioning; reinforcement learning; reward prediction error; simultaneous conditioning.
Copyright © 2021 Prével and Krebs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Arcediano F., Miller R. R. (2002). Some constraints for models of timing: a temporal coding hypothesis perspective. Learn. Motiv. 33, 105–123. 10.1006/lmot.2001.1102 - DOI
-
- Barnet R. C., Arnold H. M., Miller R. R. (1991). Simultaneous conditioning demonstrated in second-order conditioning: evidence for similar associative structure in forward and simultaneous conditioning. Learn. Motiv. 22, 253–268. 10.1016/0023-9690(91)90008-V - DOI
-
- Barnet R. C., Cole R. P., Miller R. R. (1997). Temporal integration in second-order conditioning and sensory preconditioning. Anim. Learn. Behav. 25, 221–233. 10.3758/BF03199061 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

