Antioxidant Activity In Vitro Guided Screening and Identification of Flavonoids Antioxidants in the Extract from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg
- PMID: 34858501
- PMCID: PMC8632396
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/7195125
Antioxidant Activity In Vitro Guided Screening and Identification of Flavonoids Antioxidants in the Extract from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg
Abstract
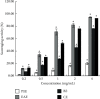
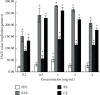
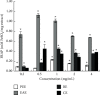
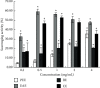
This study aimed to investigate the extract with high antioxidant activity of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg and identify the antioxidant components in vitro. α, α-Diphenyl-β-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical assay, Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) assay, ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), and hydroxyl radical scavenging method were used to screen the extract with high antioxidant activity. The antioxidant capacity of the extracts was evaluated by the free radical scavenging ability of DPPH. The ability of extracts to scavenge 2, 2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) free radical was evaluated by TEAC assay. The FRAP method was used to evaluate the ability of extracts to reduce Fe3+. The ability to scavenge hydroxyl radicals produced by the interaction of hydrogen peroxide and Fe2+ was measured by monitoring the change in the absorbance of the reaction mixture at 536 nm. Then, high-performance liquid chromatography-DPPH (HPLC-DPPH) and HPLC-hydroxyl radical scavenging methods were used to screen the antioxidant components in the extract. The molecular weight of the above antioxidant components was investigated using the qualitative analytical method of high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-Q-TOF LC/MS). Based on the concentrations of the samples (0.2-4 mg/mL), the DPPH free radical scavenging ability, ABTS+ free radical scavenging ability, hydroxyl free radical scavenging ability, and Fe3+ reducing ability of the ethyl acetate extract (EAE) were stronger than that of the crude extract (CE), petroleum ether extract (PEE), and n-butanol extract (BE). The EAE has higher antioxidant activity than CE, PEE, and BE. Six antioxidant components, rutin, quercetin, isoquercetin, astragalin, kaempferol, and kaempferol-3-o-rutoside, were identified in the EAE.
Copyright © 2021 Li Ding et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
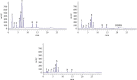
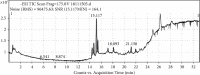

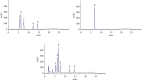
References
-
- Liao S. B., Cai W. W., Chen D., Xie P., Huang J., Mu Z. X. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of the extracts of Tetrastigmais hemsleyanum’s aerial parts form Fujian in vivo. Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy . 2017;34(2):319–324.
-
- Dan-Dan W., Rong G., Bin Y. Experimental study on the effects of Radix Tetrastigmae on respiratory syncytial virus. Natural Product Research and Development . 2019;31:1070–1074.
-
- Zhong X. M., Mao Q. Q., Huang Z. Experimental study on the protective effect and acute toxicity of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum extract on CCl4 induced acute liver injury in mice. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine . 2006;28(3):422–424.
-
- Ping L. I., Weiwei J. I., Xin P., Pathology D. O. Study on the trifolium extract in anit-induced liver injury in mice. China Modern Doctor . 2018;56(30):32–35.
-
- Wu H. Y., Wu Y. T., Chen Y. Y., Luo H. L., Jiang H. F. Effect of Radix Tetrastigma hemsleyani flavones on apoptosis and MAPK signaling pathway in myeloid leukemia NB-4 cells. Chinese Journal of Pathophysiology . 2019;35(8):1451–1456.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

