Biomarkers and Mechanism Analysis for Polygoni Multiflori Radix Preparata-Induced Liver Injury by UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS-Based Metabolomics
- PMID: 34858511
- PMCID: PMC8632464
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/7677392
Biomarkers and Mechanism Analysis for Polygoni Multiflori Radix Preparata-Induced Liver Injury by UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS-Based Metabolomics
Abstract
Background: Polygonum Multiflorum Radix Preparata (PMP), prepared from Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. (PM), is traditionally valued for its liver and kidney-tonifying effects. However, the previous studies showed that PMP was hepatotoxic, which limited its clinical use. Unfortunately, the potential hepatotoxic ingredients and the molecular mechanism are still uncertain.
Objective: The aim of this study was to find out potential biomarkers of hepatotoxicity using metabolomics profile.
Materials and methods: 60% ethanol extract of PMP (PMPE) was prepared. Subsequently, an untargeted metabolomics technology in combination with ROC curve analysis method was applied to investigate the alteration of plasma metabolites in rats after oral administration of PMPE (40 g/kg/d) for 28 days.
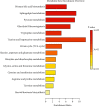
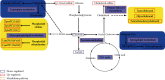
Results: Compared to the control group, the significant difference in metabolic profiling was observed in the PMPE-induced liver injury group, and sixteen highly specific biomarkers were identified. These metabolites were mainly enriched into bile acids, lipids, and energy metabolisms, indicating that PMPE-induced liver injury could be related to cholestasis and dysregulated lipid metabolism.
Conclusions: This study is contributed to understand the potential pathogenesis of PMP-induced liver injury. The metabonomic method may be a valuable tool for the clinical diagnosis of PMP-induced liver injury.
Copyright © 2021 Liming Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The assessment of the chronic hepatotoxicity induced by Polygoni Multiflori Radix in rats: A pilot study by using untargeted metabolomics method.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 May 5;203:182-190. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.03.046. Epub 2017 Mar 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28365236
-
A Serum Metabolomic Study on Rats Induced by Polygoni Multiflori Radix and Polygoni Multiflori Radix Preparata by Pattern Recognition and Pathways Analysis.Biol Pharm Bull. 2020 Feb 1;43(2):306-318. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b19-00630. Epub 2019 Nov 23. Biol Pharm Bull. 2020. PMID: 31761827
-
Study on hepatotoxicity of different dosages of Polygoni multiflori radix praeparata in rats by metabolomics based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019 Oct 25;175:112760. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2019.07.008. Epub 2019 Jul 8. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019. PMID: 31382117
-
Advances in Understanding the Metabolites and Metabolomics of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb: A Mini-review.Curr Drug Metab. 2021;22(3):165-172. doi: 10.2174/1389200221666201201091345. Curr Drug Metab. 2021. PMID: 33261537 Review.
-
Polygonum multiflorum-Induced Liver Injury: Clinical Characteristics, Risk Factors, Material Basis, Action Mechanism and Current Challenges.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Dec 13;10:1467. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01467. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31920657 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicology and detoxification of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb.: a comprehensive review.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 17;15:1427019. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1427019. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38953108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of Hepatotoxic Equivalent Markers and Mechanism of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. by Metabolomics Coupled with Molecular Docking.Molecules. 2022 Dec 21;28(1):25. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010025. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- China Pharmacopoeia Committee. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China . Beijing, China: China Pharmacopoeia Committee; 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

