Treatment of Severe Acute Pancreatitis and Related Lung Injury by Targeting Gasdermin D-Mediated Pyroptosis
- PMID: 34858995
- PMCID: PMC8632453
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.780142
Treatment of Severe Acute Pancreatitis and Related Lung Injury by Targeting Gasdermin D-Mediated Pyroptosis
Abstract
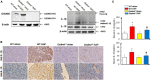
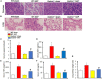
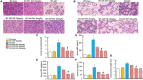
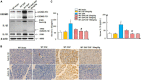
The functional relevance and effects of the pyroptosis executioner gasdermin D (GSDMD) on severe acute pancreatitis (SAP)-associated lung injury are unclear. We established caerulein-induced mouse models of SAP-associated lung injury, which showed that GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis was activated in both pancreatic and lung tissues. Compared with Gsdmd wild-type SAP mouse models, Gsdmd knockout (Gsdmd-/- ) ameliorated SAP-induced pancreas and related lung injury. Additionally, we investigated the effects of disulfiram on the treatment of SAP. Disulfiram is a Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved anti-alcoholism drug, which is reported as an effective pyroptosis inhibitor by either directly covalently modifying GSDMD or indirectly inhibiting the cleavage of GSDMD via inactivating Nod-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome. We demonstrated that disulfiram inhibited the cleavage of GSDMD, alleviated caerulein-induced SAP and related lung injury, and decreased the expression levels of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β and IL-18). Collectively, these findings disclosed the role of GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis in SAP and the potential application of disulfiram in the treatment of SAP.
Keywords: GSDMD; acute lung injury; disulfiram; inflammation; programmed cell death; pyroptosis; severe acute pancreatitis.
Copyright © 2021 Wu, Zhang, Zhao, Chen, Zhou and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

