Relationship between pre-pregnancy maternal body mass index and infant weight trajectories in HIV-exposed and HIV-unexposed infants
- PMID: 34859468
- PMCID: PMC9163208
- DOI: 10.1111/ppe.12825
Relationship between pre-pregnancy maternal body mass index and infant weight trajectories in HIV-exposed and HIV-unexposed infants
Abstract
Background: Maternal HIV and antiretroviral therapy (ART) exposure in utero may influence infant weight, but the contribution of maternal y body mass index (BMI) to early life overweight and obesity is not clear.
Objective: To estimate associations between maternal BMI at entry to antenatal care (ANC) and infant weight through approximately 1 year of age and to evaluate whether associations were modified by maternal HIV status, maternal HIV and viral load, breastfeeding intensity through 6 months or timing of entry into ANC.
Methods: We followed HIV-uninfected and -infected pregnant women initiating efavirenz-based ART from first antenatal visit through 12 months postpartum. Infant weight was assessed via World Health Organization BMI and weight-for-length z-scores (WLZ) at 6 weeks, 3, 6, 9 and 12 months. We used multivariable linear mixed-effects models to estimate associations between maternal BMI and infant z-scores over time.
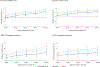
Results: In 861 HIV-uninfected infants (454 HIV-exposed; 407 HIV-unexposed), nearly 20% of infants were overweight or obese by 12 months of age, regardless of HIV exposure status. In multivariable analyses, increasing maternal BMI category was positively associated with higher infant BMIZ and WLZ scores between 6 weeks and 12 months of age and did not differ by HIV exposure status. However, HIV-exposed infants had slightly lower BMIZ and WLZ trajectories through 12 months of age, compared with HIV-unexposed infants across all maternal BMI categories. Differences in BMIZ and WLZ scores by HIV exposure were not explained by timing of entry into ANC or maternal viral load pre-ART initiation, but z-scores were slightly higher for HIV-exposed infants who were predominantly or exclusively versus partially breastfed.
Conclusions: These findings suggest maternal BMI influences early infant weight gain, regardless of infant HIV exposure status. Intervention to reduce maternal BMI may help to address growing concerns about obesity among HIV-uninfected children.
Keywords: BMI; HIV; HIV-exposed; South Africa; infant growth; infant weight.
© 2021 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
Beyond COVID-19: Equitable epidemiology for studying the impact of maternal infections on neonatal mortality and morbidity.Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2022 Jul;36(4):553-555. doi: 10.1111/ppe.12892. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2022. PMID: 35768341 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- le Roux SM, Abrams EJ, Donald KA, Brittain K, Phillips TK, Nguyen KK, et al. Growth trajectories of breastfed HIV-exposed uninfected and HIV-unexposed children under conditions of universal maternal antiretroviral therapy: a prospective study. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2019; 3:234–244. - PubMed
-
- Neri D, Somarriba GA, Schaefer NN, Chaparro AI, Scott GB, Lopez Mitnik G, et al. Growth and body composition of uninfected children exposed to human immunodeficiency virus: comparison with a contemporary cohort and United States National Standards. J Pediatr. 2013; 163:249–254 e241–242. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Patel D, Bland R, Coovadia H, Rollins N, Coutsoudis A, Newell ML. Breastfeeding, HIV status and weights in South African children: a comparison of HIV-exposed and unexposed children. AIDS. 2010; 24:437–445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

