Perioperative changes of FGF23 in patients undergoing surgery for primary hyperparathyroidism
- PMID: 34860179
- PMCID: PMC8859952
- DOI: 10.1530/EC-21-0430
Perioperative changes of FGF23 in patients undergoing surgery for primary hyperparathyroidism
Abstract
Background: Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) is a key regulator of urine phosphate excretion. The aim of the study was to investigate the perioperative (intraoperative and postoperative) changes of plasma intact and C-terminal FGF23 (iFGF23, cFGF23) concentrations in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism (pHPT) submitted to surgery.
Materials and methods: The study involved 38 adult patients with pHPT caused by adenoma. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels were investigated intraoperatively (just before the incision and 10 min after adenoma excision). cFGF23, iFGF23, phosphate, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and procollagen type 1 N-terminal propetide (P1NP) were measured intraoperatively and postoperatively (next day after the surgery).
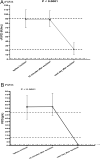
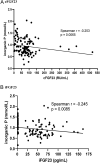
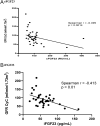
Results: PTH levels decreased intraoperatively (13.10 pmol/L vs 4.17 pmol/L, P< 0.0001). FGF23 levels measured intraoperatively were at the upper level of reference interval. cFGF23 decreased postoperatively compared with the values measured just before the incision (cFGF23: 89.17 RU/mL vs 22.23 RU/mL, P< 0.0001). iFGF23 decreased as well, but the postoperative values were low. Postoperative inorganic phosphate values increased (1.03 mmol/L vs 0.8 mmol/L, P= 0.0025). We proved significant negative correlation of perioperative FGF23 with inorganic phosphate (cFGF23: Spearman's r = -0.253, P= 0.0065; iFGF23: Spearman's r = -0.245, P= 0.0085). We also found that FGF23 values just before incision correlated with eGFR (cystatin C) (cFGF23: Spearman's r = -0.499, P= 0.0014; iFGF23: Spearman's r = -0.413, P= 0.01).
Conclusion: Intraoperative iFGF23 and cFGF23 did not change despite PTH decreased significantly. cFGF23 and iFGF23 significantly decreased 1 day after parathyroidectomy and are associated with increase of inorganic phosphate in pHPT patients. cFGF23 and iFGF23 just before incision correlated with eGFR (cystatin C). Similar results found in both iFGF23 and cFGF23 suggest that each could substitute the other.
Keywords: cFGF23; iFGF23; parathyroid adenoma; primary hyperparathyroidism.
Figures

References
-
- Rifai N, Horvath A, Wittwer C. Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics. St. Louis: Elsevier, 2018.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

