Phosphatidylserine eversion regulated by phospholipid scramblase activated by TGF-β1/Smad signaling in the early stage of kidney stone formation
- PMID: 34860265
- PMCID: PMC8784500
- DOI: 10.1007/s00240-021-01292-0
Phosphatidylserine eversion regulated by phospholipid scramblase activated by TGF-β1/Smad signaling in the early stage of kidney stone formation
Abstract
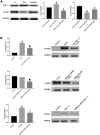
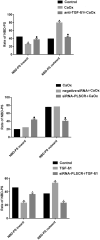
The mechanism underlying phosphatidylserine eversion in renal tubule cells following calcium oxalate-mediated damage remains unclear; therefore, we investigated the effects of TGF-β1/Smad signaling on phosphatidylserine eversion in the renal tubule cell membrane during the early stage of kidney stone development. In a rat model of early stage of calcium oxalate stone formation, phosphatidylserine eversion on the renal tubular cell membrane was detected by flow cytometry, and the expression of TGF-β1 (transforming growth factor-β1), Smad7, and phospholipid scramblase in the renal tubular cell membrane was measured by western blotting. We observed that the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway increased phosphatidylserine eversion at the organism level. The results of in vitro studies demonstrated that oxalate exposure to renal tubule cells induced TGF-β1 expression, increasing phospholipid scramblase activity and phosphatidylserine eversion in the renal tubule cell membrane. These results indicate that TGF-β1 stimulates phosphatidylserine eversion by increasing the phospholipid scramblase activity in the renal tubule cell membrane during the early stage of kidney stone development. The results of this study form a basis for further detailed research on the development of therapeutic agents that specifically treat urolithiasis and exert fewer adverse effects.
Keywords: Kidney stone; Phosphatidylserine; Phospholipid scramblase; TGF-β1.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
N-acetylcysteine regulates oxalate induced injury of renal tubular epithelial cells through CDKN2B/TGF-β/SMAD axis.Urolithiasis. 2024 Mar 23;52(1):46. doi: 10.1007/s00240-023-01527-2. Urolithiasis. 2024. PMID: 38520518
-
The differential regulation of Smad7 in kidney tubule cells by connective tissue growth factor and transforming growth factor-beta1.Nephrology (Carlton). 2007 Jun;12(3):267-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1797.2007.00788.x. Nephrology (Carlton). 2007. PMID: 17498122
-
Rosiglitazone Suppresses Calcium Oxalate Crystal Binding and Oxalate-Induced Oxidative Stress in Renal Epithelial Cells by Promoting PPAR-γ Activation and Subsequent Regulation of TGF-β1 and HGF Expression.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Nov 12;2019:4826525. doi: 10.1155/2019/4826525. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31781338 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β/Smad signaling in kidney disease.Semin Nephrol. 2012 May;32(3):236-43. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2012.04.002. Semin Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22835454 Review.
-
TGF-β signaling via TAK1 pathway: role in kidney fibrosis.Semin Nephrol. 2012 May;32(3):244-52. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2012.04.003. Semin Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22835455 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Detsyk O, Solomchak D, Bugro V. Patient pathways as a tool of improvement in management of urgent and scheduled health care for kidney stone disease. Wiad Lek. 2019;72:2128–2134. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

