Insufficient response to mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine and high incidence of severe COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients during pandemic
- PMID: 34860470
- PMCID: PMC9906453
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.16902
Insufficient response to mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine and high incidence of severe COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients during pandemic
Abstract
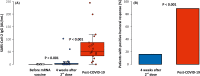
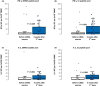
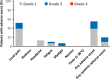
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) mRNA vaccination may fail to sufficiently protect transplant recipients against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We retrospectively evaluated COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients (n = 226) after BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine administration. The control group consisted of unvaccinated patients (n = 194) during the previous pandemic wave. We measured anti-spike protein immunoglobulin G (IgG) levels and cellular responses, using enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot assay, in a prospective cohort after vaccination (n = 31) and recovery from COVID-19 (n = 19). COVID-19 was diagnosed in 37 (16%) vaccinated and 43 (22%) unvaccinated patients. COVID-19 severity was similar in both groups, with patients exhibiting a comparable need for hospitalization (41% vs. 40%, p = 1.000) and mortality (14% vs. 9%, p = .726). Short posttransplant periods were associated with COVID-19 after vaccination (p < .001). Only 5 (16%) patients achieved positive SARS-CoV-2 IgG after vaccination, and 17 (89%, p < .001) recovered from COVID-19 (median IgG levels, 0.6 vs. 52.5 AU/ml, p < .001). A cellular response following vaccination was present in the majority (n = 22, 71%), with an increase in interleukin 2 secreting T cells (p < .001). Despite detectable T cell immunity after mRNA vaccination, kidney transplant recipients remained at a high risk of severe COVID-19. Humoral responses induced by vaccination were significantly lower than that after COVID-19.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19; clinical research / practice; infection and infectious agents - viral; infectious disease; kidney transplantation / nephrology; vaccine.
© 2021 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Figures

Comment in
-
Background risk should be taken into account when reporting vaccine effectiveness.Am J Transplant. 2022 Jul;22(7):1927-1928. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16961. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Am J Transplant. 2022. PMID: 35043536 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

