Britanin relieves ferroptosis-mediated myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion damage by upregulating GPX4 through activation of AMPK/GSK3β/Nrf2 signalling
- PMID: 34860639
- PMCID: PMC8648013
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2021.2007269
Britanin relieves ferroptosis-mediated myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion damage by upregulating GPX4 through activation of AMPK/GSK3β/Nrf2 signalling
Abstract
Context: Ferroptosis was described as an important contributor to the myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion (MIR) injury, and britanin (Bri) was reported to exert antitumor and anti-inflammatory activities.
Objective: Our study explores the effect and mechanism of Bri on MIR damage.
Materials and methods: The rat model of MIR was established by ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery. Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were divided into three groups: sham group (n = 6), MIR group (n = 6) and MIR + Bri group (n = 6; 50 mg/kg). Rats were intragastrically pre-treated with Bri or normal saline once daily for 3 days. To further verify the role and mechanism of Bri, H9C2 cells were subjected to hypoxia plus reoxygenation (H/R) to induce the in vitro model of MIR.
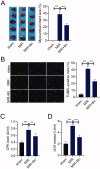
Results: Compared with MIR rats, Bri significantly decreased infarct area (22.50% vs. 38.67%), myocardial apoptosis (23.00% vs. 41.5%), creatine phosphokinase (0.57 U/mL vs. 0.76 U/mL), and lactate dehydrogenase levels (3.18 U/mL vs. 5.17 U/mL), concomitant with alleviation of ferroptosis. Mechanistically, Bri treatment induced the activation of the adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase (AMPK)/glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β)/nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway in vivo. In addition, the AMPK/GSK3β/Nrf2 pathway participated in the regulation of glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) expression, and silencing of Nrf2 attenuated the effect of Bri on H/R-induced cell injury.
Discussion and conclusions: Bri protected against ferroptosis-mediated MIR damage by upregulating GPX4 through activation of the AMPK/GSK3β/Nrf2 signalling, suggesting that Bri might become a novel therapeutic agent for MIR.
Keywords: Myocardial infarction; apoptosis; hypoxia-reoxygenation injury; iron; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures




References
-
- Barančík M, Grešová L, Barteková M, Dovinová I.. 2016. Nrf2 as a key player of redox regulation in cardiovascular diseases. Physiol Res. 65 Suppl 1:S1–S10. - PubMed
-
- Chi HJ, Chen ML, Yang XC, Lin XM, Sun H, Zhao WS, Qi D, Dong JL, Cai J.. 2017. Progress in therapies for myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. Curr Drug Targets. 18(15):1712–1721. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
