A Simplified Process for Purification and Refolding of Recombinant Human Interferon-α2b
- PMID: 34861751
- PMCID: PMC8784902
- DOI: 10.52547/ibj.26.1.85
A Simplified Process for Purification and Refolding of Recombinant Human Interferon-α2b
Abstract
Background: Interferon α-2b is a vital biotherapeutic produced through the recombinant DNA technology in E. coli. The recombinant IFN-α2b normally appears as intercellular IBs, which requires intensive refolding and purification steps.
Method: Purification of IFN-α2b from solubilized IB was performed using two-phase extraction. To optimize refolding conditions, the effects of pH and different additives, including cysteine, cystine, urea, glycerol, Triton X-100, NaCl, and arginine, were investigated. Optimal refolding buffer (0.64 mM of urea, 5.57 mM of cysteine , and 1.8 mM of cystine) was obtained using RSM. The refolding process was performed by an optimized refolding buffer in the dilution and fed-batch refolding method at different protein concentrations (25-1000 µg/mL).
Result: At a final protein concentration of 500 µg/mL, the fed-batch refolding method yielded in a biological activity of 2.24 × 108 IU/mg, which was nearly twice that of dilution method.
Conclusion: Fed-batch refolding method resulted in the biologically active IFN-α2b with high purity, which can be used for research and industrial purposes.
Keywords: Inclusion bodies; Interferon alpha-2b; Protein refolding.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

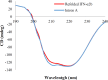
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
