A deep learning framework identifies dimensional representations of Alzheimer's Disease from brain structure
- PMID: 34862382
- PMCID: PMC8642554
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-26703-z
A deep learning framework identifies dimensional representations of Alzheimer's Disease from brain structure
Abstract
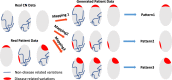
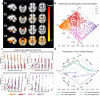
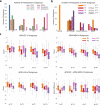
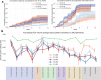
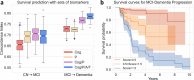
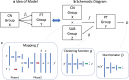
Heterogeneity of brain diseases is a challenge for precision diagnosis/prognosis. We describe and validate Smile-GAN (SeMI-supervised cLustEring-Generative Adversarial Network), a semi-supervised deep-clustering method, which examines neuroanatomical heterogeneity contrasted against normal brain structure, to identify disease subtypes through neuroimaging signatures. When applied to regional volumes derived from T1-weighted MRI (two studies; 2,832 participants; 8,146 scans) including cognitively normal individuals and those with cognitive impairment and dementia, Smile-GAN identified four patterns or axes of neurodegeneration. Applying this framework to longitudinal data revealed two distinct progression pathways. Measures of expression of these patterns predicted the pathway and rate of future neurodegeneration. Pattern expression offered complementary performance to amyloid/tau in predicting clinical progression. These deep-learning derived biomarkers offer potential for precision diagnostics and targeted clinical trial recruitment.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We disclose here that I.N. served as an educational speaker for Biogen. The remaining authors declare no competing interests
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U19 AG033655/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066462/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG059869/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG054409/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD023495/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072947/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072979/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066507/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN271201600059C/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG071514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG068057/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG052409/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States

