Edema-like symptoms are common in ultra-distance cyclists and driven by overdrinking, use of analgesics and female sex - a study of 919 athletes
- PMID: 34863204
- PMCID: PMC8643017
- DOI: 10.1186/s12970-021-00470-0
Edema-like symptoms are common in ultra-distance cyclists and driven by overdrinking, use of analgesics and female sex - a study of 919 athletes
Abstract
Background: Ultra-endurance cyclists regularly report various extents of bodily decline during long-distance bicycle rides, including potential kidney function-related symptoms such as swelling of body parts and urine changes. This study aimed to assess the prevalence of these symptoms in a representative cohort of ultra-endurance cyclists and shed light on potential predictors related to the ride, the rider and the rider's behavior.
Methods: Between November 26 and December 14, 2020, 1350 people participated in an online survey investigating potential kidney-related symptoms of ultra-distance cycling. Frequency and severity of edema-like ("swelling") symptoms and perceived changes in urine output, concentration and quality were associated with ride-related factors, demographic parameters and rider behavior-related variables.
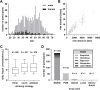
Results: A total of 919 participants met the predefined inclusion criteria. The majority (N = 603, 65.6%) stated that they suffered from at least one potential kidney function-related symptom, out of which 498 (54.2%) stated one or more edema-like ("swelling") symptoms. In correlational and multiple regression analyses, female sex, intake of analgesics and drinking strategies correlated with swelling symptoms. Further analyses indicated that drinking due to thirst and/or drinking adapted to ambient sweating and temperature negatively correlated with swelling symptoms, whereas "drinking as much as possible" enhanced these. Intake of analgesics was moderately positively correlated with swelling symptoms.
Conclusions: According to our survey, edema-like symptoms occur in the majority of ultra-distance cyclists and female sex, drinking strategy and intake of analgesic drugs are major predictors thereof. Studies are needed to investigate the underlying pathophysiological processes of such symptoms.
Keywords: Cycling; Endurance sports; Exercise-associated hyponatremia; Peripheral edema; Ultra-distance cycling.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
At the time of manuscript preparation, JSK and FRK are active ultra-distance cyclists. Other than that, the authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
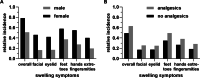
References
-
- McCubbin AJ, Cox GR, Costa RJS. Sodium intake beliefs, information sources, and intended practices of endurance athletes before and during exercise. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2019;29(4):371–381. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
