Lenzilumab in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 pneumonia (LIVE-AIR): a phase 3, randomised, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 34863332
- PMCID: PMC8635458
- DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00494-X
Lenzilumab in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 pneumonia (LIVE-AIR): a phase 3, randomised, placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
Background: The pathophysiology of COVID-19 includes immune-mediated hyperinflammation, which could potentially lead to respiratory failure and death. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) is among cytokines that contribute to the inflammatory processes. Lenzilumab, a GM-CSF neutralising monoclonal antibody, was investigated in the LIVE-AIR trial to assess its efficacy and safety in treating COVID-19 beyond available treatments.
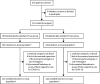
Methods: In LIVE-AIR, a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, hospitalised adult patients with COVID-19 pneumonia not requiring invasive mechanical ventilation were recruited from 29 sites in the USA and Brazil and were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive three intravenous doses of lenzilumab (600 mg per dose) or placebo delivered 8 h apart. All patients received standard supportive care, including the use of remdesivir and corticosteroids. Patients were stratified at randomisation by age and disease severity. The primary endpoint was survival without invasive mechanical ventilation to day 28 in the modified intention-to-treat population (mITT), comprising all randomised participants who received at least one dose of study drug under the documented supervision of the principal investigator or sub-investigator. Adverse events were assessed in all patients who received at least one dose of study drug. This trial is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04351152, and is completed.
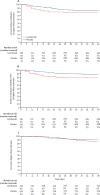
Findings: Patients were enrolled from May 5, 2020, until Jan 27, 2021. 528 patients were screened, of whom 520 were randomly assigned and included in the intention-to-treat population. 479 of these patients (n=236, lenzilumab; n=243, placebo) were included in the mITT analysis for the primary outcome. Baseline demographics were similar between groups. 311 (65%) participants were males, mean age was 61 (SD 14) years at baseline, and median C-reactive protein concentration was 79 (IQR 41-137) mg/L. Steroids were administered to 449 (94%) patients and remdesivir to 347 (72%) patients; 331 (69%) patients received both treatments. Survival without invasive mechanical ventilation to day 28 was achieved in 198 (84%; 95% CI 79-89) participants in the lenzilumab group and in 190 (78%; 72-83) patients in the placebo group, and the likelihood of survival was greater with lenzilumab than placebo (hazard ratio 1·54; 95% CI 1·02-2·32; p=0·040). 68 (27%) of 255 patients in the lenzilumab group and 84 (33%) of 257 patients in the placebo group experienced at least one adverse event that was at least grade 3 in severity based on CTCAE criteria. The most common treatment-emergent adverse events of grade 3 or higher were related to respiratory disorders (26%) and cardiac disorders (6%) and none led to death.
Interpretation: Lenzilumab significantly improved survival without invasive mechanical ventilation in hospitalised patients with COVID-19, with a safety profile similar to that of placebo. The added value of lenzilumab beyond other immunomodulators used to treat COVID-19 alongside steroids remains unknown.
Funding: Humanigen.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests ZT has received research support from Humanigen and unrestricted education support from Gilead, ViiV, and Merck (all to the institution). CRL has received research support from Gilead, Pfizer, and NIAID (ACTIV-2–A5401). VMC and WSA are third-party agency consultants to Humanigen. CP is a paid consultant to Gilead. JB has received research support from Gilead and Humanigen. CFK has received research support grants (to the institution) from NIH, CDC, Gilead Sciences, and ViiV. VCM has received investigator-initiated research grants (to the institution) and consultation fees (both unrelated to the current work) from Eli Lilly, Bayer, Gilead Sciences, and ViiV. CD, DC, OA, and GC are employees of, or consultants to, Humanigen. ADB is supported by grants from NIAID (AI110173 and AI120698), Amfar (#109593), and Mayo Clinic (HH Sheikh Khalifa Bin Zayed Al-Nahyan Professorship of Infectious Diseases); he is a paid consultant for AbbVie and Flambeau Diagnostics, is a paid member of the DSMB for Corvus Pharmaceuticals, Equilium, and Excision Biotherapeutics, has received fees for speaking for Reach MD, owns equity for scientific advisory work in Zentalis and Nference, and is founder and President of Splissen Therapeutics. CDB and RO declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Stimulating severe COVID-19: the potential role of GM-CSF antagonism.Lancet Respir Med. 2022 Mar;10(3):223-224. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00539-7. Epub 2021 Dec 1. Lancet Respir Med. 2022. PMID: 34863335 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
In inpatients with COVID-19 who need supplemental oxygen, lenzilumab increased ventilation-free survival.Ann Intern Med. 2022 Apr;175(4):JC39. doi: 10.7326/J22-0019. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Ann Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 35377717
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

