Multicenter validation of Early Warning Scores for detection of clinical deterioration in COVID-19 hospitalized patients
- PMID: 34866728
- PMCID: PMC8629741
- DOI: 10.1016/j.medin.2021.11.002
Multicenter validation of Early Warning Scores for detection of clinical deterioration in COVID-19 hospitalized patients
Abstract
Objective: Investigate the predictive value of NEWS2, NEWS-C, and COVID-19 Severity Index for predicting intensive care unit (ICU) transfer in the next 24 h.
Design: Retrospective multicenter study.
Setting: Two third-level hospitals in Argentina.
Patients: All adult patients with confirmed COVID-19, admitted on general wards, excluding patients with non-intubated orders.
Interventions: Patients were divided between those who were admitted to ICU and non-admitted. We calculated the three scores for each day of hospitalization.
Variables: We evaluate the calibration and discrimination of the three scores for the outcome ICU admission within 24, 48 h, and at hospital admission.
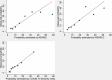
Results: We evaluate 13,768 days of hospitalizations on general medical wards of 1318 patients. Among these, 126 (9.5%) were transferred to ICU. The AUROC of NEWS2 was 0.73 (95%CI 0.68-0.78) 24 h before ICU admission, and 0.52 (95%CI 0.47-0.57) at hospital admission. The AUROC of NEWS-C was 0.73 (95%CI 0.68-0.78) and 0.52 (95%CI 0.47-0.57) respectively, and the AUROC of COVID-19 Severity Index was 0.80 (95%CI 0.77-0.84) and 0.61 (95%CI 0.58-0.66) respectively. COVID-19 Severity Index presented better calibration than NEWS2 and NEWS-C.
Conclusion: COVID-19 Severity index has better calibration and discrimination than NEWS2 and NEWS-C to predict ICU transfer during hospitalization.
Objetivo: Investigar el valor predictivo de los scores NEWS2, NEWS-C y COVID-19 Severity Index para predecir la transferencia de urgencia a la unidad de cuidados intensivos (UCI) en las próximas 24 horas.
Diseño: Estudio multicéntrico retrospectivo.
Ámbito: Dos hospitales de tercer nivel en Argentina.
Pacientes: Pacientes adultos con COVID-19, ingresados en salas generales, excluyendo pacientes con órdenes de no intubar.
Intervenciones: Se dividió a los pacientes entre los que ingresaron en la UCI y los que no ingresaron. Calculamos las tres puntuaciones para cada día de hospitalización.
Variables: Evaluamos la calibración y discriminación de las tres puntuaciones para predecir el traslado de urgencia a UCI en las 24, 48 h previas al pase a UCI y al ingreso hospitalario.
Resultados: Evaluamos 13.768 días de hospitalización en internación general de 1.318 pacientes, de los cuales 126 (9,5%) fueron trasladados a UCI. El AUROC del NEWS2 fue de 0,73 (IC 95% 0,68-0,78) 24 h antes del ingreso en UCI y de 0,52 (IC 95% 0,47-0,57) al ingreso hospitalario. El AUROC de NEWS-C fue de 0,73 (IC 95% 0,68-0,78) y 0,52 (IC 95% 0,47-0,57) respectivamente, y el AUROC del COVID-19 Severity Index fue de 0,80 (IC 95% 0,77-0,84) y 0,61 (IC 95% 0,58-0,66) respectivamente. El COVID-19 Severity Index presentó una mejor calibración que NEWS2 y NEWS-C.
Conclusión: El COVID-19 Severity Index presentó una mejor calibración y discriminación que NEWS2 y NEWS-C para predecir la transferencia de la UCI durante la hospitalización.
Keywords: COVID-19; Critical care; Early Warning Score; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2021 Elsevier España, S.L.U. y SEMICYUC. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Alam N., Hobbelink E.L., van Tienhoven A.J., van de Ven P.M., Jansma E.P., Nanayakkara P.W.B. The impact of the use of the Early Warning Score (EWS) on patient outcomes: a systematic review. Resuscitation. 2014;85:587–594. - PubMed
-
- National Early Warning Score (NEWS) 2, NEWS2 and deterioration in COVID-19; 2021. https://www.rcplondon.ac.uk/news/news2-and-deterioration-covid-19 [consulted 5.11.21].
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous