Acaudina molpadioides mediates lipid uptake by suppressing PCSK9 transcription and increasing LDL receptor in human liver cells
- PMID: 34867013
- PMCID: PMC8626262
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.08.003
Acaudina molpadioides mediates lipid uptake by suppressing PCSK9 transcription and increasing LDL receptor in human liver cells
Abstract
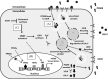
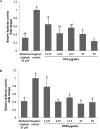
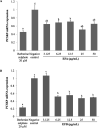
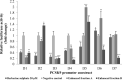
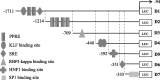
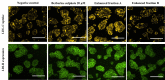
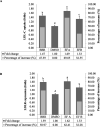
Acaudina molpadioides has been long used as traditional medicinal resources and reported to demonstrate various important bioactivities such as anticoagulation, antithrombosis, anti-hyperglycemia and anticancer. However, its lipid lowering activity is yet to be fully explored. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) is an enzyme that enhances the lysosomal degradation of hepatic low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) resulting in excessive accumulation of the plasma levels of LDL-cholesterols (LDL-C) which subsequently accelerate atherosclerosis. In the present study, A. molpadioides fractions were subjected to promoter-reporter luciferase assay to determine its role as PCSK9 inhibitors. It was found both fractions (EFA and EFB) reduced the transcriptional activity of PCSK9 promoter. Among the seven 5'end deletion constructs of PCSK9 promoter, fragments D1 (-1,711/-94), D3 (-709/-94) and D4 (-440/-94), were suppressed in the presence of both fractions whereas D2 (-1,214/-94), and, D6 (-351/-94) as well as D7 (-335/-94) were inhibited only by EFA and EFB, respectively. Further transcription factor binding sites prediction using MatInspector software discovered various potential cis-regulatory elements namely, PPAR, KLFs, RBPJ-kappa and SREBP that may potentially be involved in ameliorating the transcriptional activity of PCSK9. Immunofluorescence staining was used to evaluate the effects of both fractions on LDL-C and LDLR. Results showed that levels of LDL-C uptake in EFA-treated cells were 69.1% followed by EFB at 32.6%, as compared to untreated control after 24 h treatment. The LDLR protein distribution was induced by 62.41% and 32.2%, which corresponded to an increase in LDL-C uptake in both EFA and EFB treatment, respectively. Hence, the inhibition of PCSK9 by bioactive compounds in EFA and EFB could be another promising therapeutic agent in reducing the cholesterol levels and atherosclerosis by targeting PCSK9.
Keywords: Acaudina molpadioides; Atherosclerosis; Low density lipoprotein; PCSK9; Promoter-reporter based assay.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Abifadel M., Varret M., Rabès J.-P., Allard D., Ouguerram K., Devillers M., Cruaud C., Benjannet S., Wickham L., Erlich D., Derré A., Villéger L., Farnier M., Beucler I., Bruckert E., Chambaz J., Chanu B., Lecerf J.-M., Luc G., Moulin P., Weissenbach J., Prat A., Krempf M., Junien C., Seidah N.G., Boileau C. Mutations in PCSK9 cause autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia. Nat. Genet. 2003;34(2):154–156. doi: 10.1038/ng1161. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Adams M., Reginato M.J., Shao D., Lazar M.A., Chatterjee V.K. Transcriptional activation by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ is inhibited by phosphorylation at a consensus mitogen-activated protein kinase site. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272(8):5128–5132. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.8.5128. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Allard D., Amsellem S., Abifadel M., Trillard M., Devillers M., Luc G., Krempf M., Reznik Y., Girardet J.-P., Fredenrich A., Junien C., Varret M., Boileau C., Benlian P., Rabès J.-P. Novel mutations of the PCSK9 gene cause variable phenotype of autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia. Hum. Mutat. 2005;26(5):497. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1098-100410.1002/humu.v26:510.1002/humu.9383. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Azemi N.A., Ismail N., Abu-Baka L., Tengku Muhammad T.S. Sterol composition and anti-atherosclerosis effects of Xestospongia muta extracts by increasing transcriptional activity of SR-B1 promoter. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2019;10:2892–2897. doi: 10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.10(6).2892-97. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

