The Risk of Nephropathy, Retinopathy, and Leg Amputation in Patients With Diabetes and Hypertension: A Nationwide, Population-Based Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 34867799
- PMCID: PMC8637105
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.756189
The Risk of Nephropathy, Retinopathy, and Leg Amputation in Patients With Diabetes and Hypertension: A Nationwide, Population-Based Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the risks of chronic kidney disease (CKD), end-stage renal disease (ESRD), sight-threatening retinopathy, and leg amputation between patients with diabetes or hypertension.
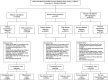
Methods: From January 1, 2000, to December 31, 2015, we identified 28943 matched pairs of patients with diabetes with and without subsequent hypertension, 89102 pairs of patients with hypertension with and without subsequent diabetes, and 145294 pairs of patients with coexisting diabetes and hypertension with a previous history of diabetes or hypertension from Taiwan's National Health Insurance Research Database. Cox proportional-hazard models were used for calculating the risks of CKD, sight-threatening retinopathy, and leg amputation.
Results: The mean follow-up time of this study in different cohorts was between 3.59 and 4.28 years. In diabetes patients with vs. without subsequent hypertension, hypertension patients with vs. without subsequent diabetes, and comorbid diabetes and hypertension patients with previous diabetes vs. with previous hypertension, the adjusted HRs (95% CIs) for CKD were 2.77 (2.61-2.94), 1.73 (1.68-1.77), and 1.04 (1.02-1.07); for ESRD were 42.38 (22.62-79.4), 2.76 (2.43-3.13), and 0.72 (0.66-0.79); for sight-threatening retinopathy were 2.07 (1.85-2.3), 3.41 (3.14-3.71), and for leg amputation were 1.51 (1.43-1.58); and 4.74 (3.02-7.43), 6.27(4.72-8.31), and 1.19(1.03-1.38).
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that both diabetes and hypertension are risk factors for the development of CKD, retinopathy, and amputation. Tracing subsequent diabetes for patients with hypertension, and hypertension for patients with diabetes are important in clinical settings.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; diabetes and hypertension; end-stage renal disease; leg amputation; sight-threatening retinopathy.
Copyright © 2021 Yen, Wei, Shih, Hsu and Hwu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- GBD 2019 . Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, Global Health Data Exchange, Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 (GBD 2019) Data Resources, GBD Results Tool, Terms and Conditions (2019). Available at: http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool (Accessed May 7, 2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical