Is the Occurrence or Reversal of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Associated with Long-Term Helicobacter pylori Infection among Chinese Adults? A Cohort Study
- PMID: 34868307
- PMCID: PMC8635906
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6696473
Is the Occurrence or Reversal of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Associated with Long-Term Helicobacter pylori Infection among Chinese Adults? A Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have suggested a link between Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), yet long-term follow-up studies to elucidate this association are lacking. We aimed to identify the relationship between NAFLD and H. pylori in these people.
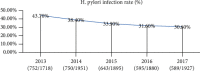
Methods: A total of 2,934 adults between June 2013 and October 2017 were collected; among them, 675 people met the requirements. People were assessed for H. pylori infection diagnosis as detected by the carbon-13 urea breath test; they were also assessed for NAFLD diagnosis by ultrasound.
Results: H. pylori infection was present in 206 patients (30.5%), and 469 (69.5%) participants were classified as controls. Participants with H. pylori infection had a higher rate of incident NAFLD than those who were uninfected (37/206; 18% versus 73/469; 15.6%) (p < 0.001). Compared with the control group, the recovery rate of NAFLD in the H. pylori+ve group was low (6/206, 2.9% versus 33/469, 7.0%) (p < 0.001). Besides, the incidence of uric acid, postprandial blood glucose, TG, LDL-C, HDL-C, and fasting plasma glucose was significantly different between the two groups (p < 0.001), but no difference was found in alanine aminotransferase (ALT), liver-total protein, urea nitrogen, and cholesterol (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: H. pylori infection was a risk factor for NAFLD and affected the occurrence or reversal of NAFLD, indicating that H. pylori infection eradication might play a role in reducing the risk of NAFLD.
Copyright © 2021 Xia-Xia Zhao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest related to the manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Kountouras J., Papaefthymiou A., Doulberis M., Polyzos S. A. Influence of Helicobacter pylori-connected metabolic syndrome on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its related colorectal neoplasm high risk. Liver international: official journal of the International Association for the Study of the Liver . 2020;40(2):475–476. doi: 10.1111/liv.14264. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous