Relationship between waist circumference and cardiorespiratory fitness in Chinese children and adolescents: Results from a cross-sectional survey
- PMID: 34868324
- PMCID: PMC8605195
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jesf.2021.10.004
Relationship between waist circumference and cardiorespiratory fitness in Chinese children and adolescents: Results from a cross-sectional survey
Abstract
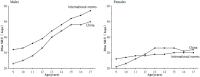
Background: This article assessed the relationship between waist circumference (WC) and cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) of children and adolescents aged 7-18 years.
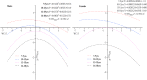
Methods: Using a stratified cluster random sampling method, 92,574 children and adolescents (47,364 males and 45,210 females) were extracted. CRF was measured by performance in the 20 m shuttle run test (20mSRT) and the subsequent estimation of maximal oxygen consumption ( O2max) using the Léger equations. Participants were divided into five groups of WC percentiles and three groups of CRF percentiles by the Lambda Mu Sigma (LMS). The correlation between WC and CRF was examined by one-way ANOVA and curvilinear regression analysis.
Results: WC increased with age, while O2max showed an age-related decline. Controlling for gender, urban, and rural factors, for children and adolescents aged 10-12, 13-15, and 16-18 years, the O2max Z-score of the normal WC group was significantly higher than the very low WC group (P < 0.05). Controlling for gender, urban, and rural factors, for participants aged 7-18 years, the O2max Z-score of the normal WC group was significantly higher than the high WC group and the very high WC group (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: It generally shows a "parabolic" trend between WC-Z and O2max-Z. The CRF among children and adolescents in the normal WC group is significantly higher than that in the low and the high WC groups.
Keywords: 20 m shuttle Run test; Cardiorespiratory fitness; Children and adolescents; Maximal oxygen consumption; Waist circumference.
© 2021 The Society of Chinese Scholars on Exercise Physiology and Fitness. Published by Elsevier (Singapore) Pte Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Yin X.J. Cardiorespiratory fitness is an important dimension of physical fitness in children and adolescents. Chin J Sch Health. 2017;38(12):1761–1764. ([In Chinese, English abstract])
-
- World Health Organization https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight Avaiable online. accessed: July 2020.
-
- Brand C., Reuter C.P., Gaya A.R., et al. Association between cardiorespiratory fitness and cardiometabolic risk factors in Brazilian children and adolescents: the mediating role of obesity parameters. Paediatr Int Child Health. 2021;41(2):93–102. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

