Prevalence of Erectile Dysfunction and Associated Factors among Hypertensive Patients Attending Governmental Health Institutions in Gondar City, Northwest Ethiopia: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 34868672
- PMCID: PMC8642021
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/1482500
Prevalence of Erectile Dysfunction and Associated Factors among Hypertensive Patients Attending Governmental Health Institutions in Gondar City, Northwest Ethiopia: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Introduction: Erectile dysfunction is a common sexual problem affecting men with hypertension. It may result in withdrawal from sexual engagement, decreased work productivity, psychosocial problems including poor self-esteem and depression, and reduction in quality of life for both the affected men and their female partners.
Objective: This study was aimed to determine the prevalence of erectile dysfunction and associated factors among hypertensive patients attending governmental health institutions in Gondar city, Northwest Ethiopia.
Materials and methods: An institutional-based cross-sectional study was conducted on 423 hypertensive men randomly selected using a systematic random sampling technique. Erectile dysfunction was assessed using the International Index of Erectile Function-5 tool. Sociodemographic, clinical, and behavioral factors were also collected using pretested interviewer-administered questionnaires. Data were entered into EpiData version 4.6 and analyzed using Stata-14. Binary logistic regression was performed to identify factors associated with erectile dysfunction. The level of significance was computed at a p value ≤ 0.05.
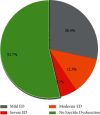
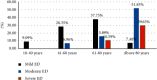
Results: The mean age of the study participants was 58.84 ± 13.52 years. The prevalence of erectile dysfunction among hypertensive men was 46.34% (95% CI: 41.61, 51.12). About 28% of them had a mild form of erectile dysfunction while nearly 6% had severe forms. Age above 60 years (AOR = 3.8, 95% CI: 1.62, 6.55), stage II hypertension (AOR = 3.5, 95% CI: 1.63, 5.74), hypertension duration >10 years (AOR = 2.5, 95% CI:1.12, 4.19), comorbidity (AOR = 1.7, 95% CI: 1.04, 3.15), depression (AOR = 2.35, 95% CI: 1.31, 4.21), and being physically active (AOR = 0.48, 95% CI: 0.28, 0.83) were factors significantly associated with erectile dysfunction.
Conclusion: Nearly half of the study participants had some form of erectile dysfunction, indicating the presence of a high burden of the problem. Assessment of hypertensive men for erectile dysfunction should be part of routine medical care.
Copyright © 2021 Deribew Abebaw Abuhay et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sexual dysfunction and its associated factors among patients with heart failure in public hospitals in Gondar town, North and West Gondar, 2024.Reprod Health. 2024 Oct 16;21(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s12978-024-01883-1. Reprod Health. 2024. PMID: 39415255 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and determinants of erectile dysfunction among diabetic patients attending in hospitals of central and northwestern zone of Tigray, northern Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2017 Mar 15;17(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12902-017-0167-5. BMC Endocr Disord. 2017. PMID: 28298205 Free PMC article.
-
Erectile dysfunction and its associated factors among the male population in Adigrat Town, Tigrai Region, Ethiopia: A cross-sectional study.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 19;16(3):e0242335. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242335. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33740010 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual dysfunction among men with diabetes mellitus attending chronic out-patient department at the three hospitals of Northwest Amhara region, Ethiopia: Prevalence and associated factors.PLoS One. 2021 Aug 11;16(8):e0256015. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256015. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34379695 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors of erectile dysfunction among diabetes patients in Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Transl Endocrinol. 2020 Jul 3;21:100232. doi: 10.1016/j.jcte.2020.100232. eCollection 2020 Sep. J Clin Transl Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32685380 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Diosdado-Figueiredo M., Balboa-Barreiro V., Pértega-Diaz S., Seoane-Pillado T., Pita-Fernández S., Chantada-Abal V. Erectile dysfunction in patients with arterial hypertension. Cardiovascular risk and impact on their quality of life. Medicina Clínica . 2019;152(6):209–215. doi: 10.1016/j.medcle.2018.05.056. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

