MiR-489-3p Reduced Pancreatic Cancer Proliferation and Metastasis By Targeting PKM2 and LDHA Involving Glycolysis
- PMID: 34868902
- PMCID: PMC8632778
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.651535
MiR-489-3p Reduced Pancreatic Cancer Proliferation and Metastasis By Targeting PKM2 and LDHA Involving Glycolysis
Abstract
Introduction: Malignant proliferation and metastasis are some of the causes of high mortality in pancreatic cancer. MicroRNAs have been a hot spot in cancer research and are involved in tumor formation and metabolic stress responses. However, the biology function and underlying mechanism of miRNA regulating pancreatic cancer progress is remained uncleared.
Methods: RNA-seq analysis the glycolysis associated miRNAs and verified miRNA-489-3p was involving in glycolysis. We used RNA in situ hybridization (ISH) and qRT-PCR to analyze the differential expression of miR-489-3p in pancreatic cancer tissues and adjacent tissues and cell lines. Then the function assay of in vivo and in vitro were used to evaluated the role of miR-489-3p in the proliferation, metastasis and glucose metabolism of pancreatic cancer. Furthermore, dual luciferase reporter and rescue experiments were performed to explore the mechanism underlying in the role of miRNA-489-3p.
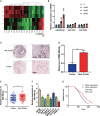
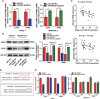
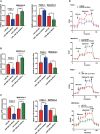
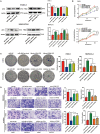
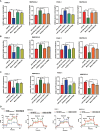
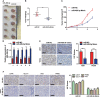
Results: We determined that glycolysis associated miRNA miR-489-3p was downregulated in pancreatic cancer tissues and cell lines. The gain and loos of function experiments confirmed that miR-489-3p could inhibit the proliferation, metastasis and glucose metabolism of pancreatic cancer. Further, we found that miR-489-3p could target regulating LDHA and PKM through the luciferase report experiment. Finally, in vivo experiment confirmed that highly expressed miR-489-3p inhibited the growth of pancreatic cancer.
Conclusion: In short, this study identified miR-489-3p as a novel therapy target for pancreatic cancer which was involving in the proliferation, metastasis and glycolysis, but its diagnostic value deserves further study.
Keywords: glycolysis; metastasis; miR-489-3p; pancreatic cancer; proliferation.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, He, Shen, Wang, Liu and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

