Diagnostic Performance of 2D and 3D T2WI-Based Radiomics Features With Machine Learning Algorithms to Distinguish Solid Solitary Pulmonary Lesion
- PMID: 34868905
- PMCID: PMC8637439
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.683587
Diagnostic Performance of 2D and 3D T2WI-Based Radiomics Features With Machine Learning Algorithms to Distinguish Solid Solitary Pulmonary Lesion
Abstract
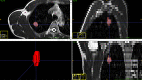
Objective: To evaluate the performance of 2D and 3D radiomics features with different machine learning approaches to classify SPLs based on magnetic resonance(MR) T2 weighted imaging (T2WI).
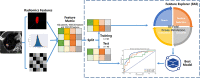
Material and methods: A total of 132 patients with pathologically confirmed SPLs were examined and randomly divided into training (n = 92) and test datasets (n = 40). A total of 1692 3D and 1231 2D radiomics features per patient were extracted. Both radiomics features and clinical data were evaluated. A total of 1260 classification models, comprising 3 normalization methods, 2 dimension reduction algorithms, 3 feature selection methods, and 10 classifiers with 7 different feature numbers (confined to 3-9), were compared. The ten-fold cross-validation on the training dataset was applied to choose the candidate final model. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), precision-recall plot, and Matthews Correlation Coefficient were used to evaluate the performance of machine learning approaches.
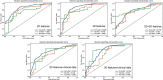
Results: The 3D features were significantly superior to 2D features, showing much more machine learning combinations with AUC greater than 0.7 in both validation and test groups (129 vs. 11). The feature selection method Analysis of Variance(ANOVA), Recursive Feature Elimination(RFE) and the classifier Logistic Regression(LR), Linear Discriminant Analysis(LDA), Support Vector Machine(SVM), Gaussian Process(GP) had relatively better performance. The best performance of 3D radiomics features in the test dataset (AUC = 0.824, AUC-PR = 0.927, MCC = 0.514) was higher than that of 2D features (AUC = 0.740, AUC-PR = 0.846, MCC = 0.404). The joint 3D and 2D features (AUC=0.813, AUC-PR = 0.926, MCC = 0.563) showed similar results as 3D features. Incorporating clinical features with 3D and 2D radiomics features slightly improved the AUC to 0.836 (AUC-PR = 0.918, MCC = 0.620) and 0.780 (AUC-PR = 0.900, MCC = 0.574), respectively.
Conclusions: After algorithm optimization, 2D feature-based radiomics models yield favorable results in differentiating malignant and benign SPLs, but 3D features are still preferred because of the availability of more machine learning algorithmic combinations with better performance. Feature selection methods ANOVA and RFE, and classifier LR, LDA, SVM and GP are more likely to demonstrate better diagnostic performance for 3D features in the current study.
Keywords: algorithms; area under the curve; lung neoplasms; machine learning; magnetic resonance imaging.
Copyright © 2021 Wan, Zhou, Xia, Hu, Wang, Peng, Zhang, Sun, Song, Yang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors TZ and JS were employed by Philips Healthcare. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Meier-Schroers M, Homsi R, Gieseke J, Schild HH, Thomas D. Lung Cancer Screening With MRI: Evaluation of MRI for Lung Cancer Screening by Comparison of LDCT- and MRI-Derived Lung-RADS Categories in the First Two Screening Rounds. Eur Radiol (2019) 29:898–905. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5607-8 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

