Identification of a N6-Methyladenosine (m6A)-Related lncRNA Signature for Predicting the Prognosis and Immune Landscape of Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 34868980
- PMCID: PMC8637334
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.763027
Identification of a N6-Methyladenosine (m6A)-Related lncRNA Signature for Predicting the Prognosis and Immune Landscape of Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: m6A-related lncRNAs emerged as potential targets for tumor diagnosis and treatment. This study aimed to identify m6A-regulated lncRNAs in lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) patients.
Materials and methods: RNA sequencing and the clinical data of LUSC patients were downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. The m6A-related lncRNAs were identified by using Pearson correlation assay. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were utilized to construct a risk model. The performance of the risk model was validated using Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and receiver operating characteristics (ROC). Immune estimation of LUSC was downloaded from TIMER, and the correlations between the risk score and various immune cells infiltration were analyzed using various methods. Differences in immune functions and expression of immune checkpoint inhibitors and m6A regulators between high-risk and low-risk groups were further explored. Finally, Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses were utilized to explore the biological functions of AL122125.1.
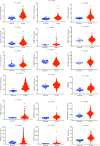
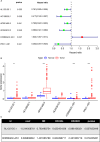
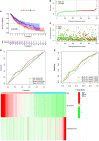
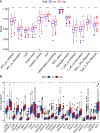
Results: A total of 351 m6A-related lncRNAs were obtained from TCGA. Seven lncRNAs demonstrated prognostic values. A further multivariate Cox regression assay constructed a risk model consisting of two lncRNAs (AL122125.1 and HORMAD2-AS1). The Kaplan-Meier analysis and area under the curve indicated that this risk model could be used to predict the prognosis of LUSC patients. The m6A-related lncRNAs were immune-associated. There were significant correlations between risk score and immune cell infiltration, immune functions, and expression of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Meanwhile, there were significant differences in the expression of m6A regulators between the high- and low-risk groups. Moreover, GO and KEGG analyses revealed that the upregulated expression of AL122125.1 was tumor-related.
Conclusion: In this study, we constructed an m6A-related lncRNA risk model to predict the survival of LUSC patients. This study could provide a novel insight to the prognosis and treatment of LUSC patients.
Keywords: immune microenvironment; long noncoding RNA; lung squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC); m6A (N6-methyladenosine); prognosis.
Copyright © 2021 Weng, Wang, Liu, Guan and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
N6-methyladenosine Modification-Related Long Non-Coding RNAs are Potential Biomarkers for Predicting the Prognosis of Patients With Osteosarcoma.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Jan-Dec;21:15330338221085354. doi: 10.1177/15330338221085354. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 35422168 Free PMC article.
-
The development and validation of a m6A-lncRNAs based prognostic model for overall survival in lung squamous cell carcinoma.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Oct;14(10):4055-4072. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-1185. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 36389308 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic analysis of ferroptosis-related long non-coding RNA predicting prognosis in patients with lung squamous cell carcinoma.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022 Apr;11(4):632-646. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-22-224. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35529787 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of tumor immune microenvironment and prognosis of m6A-related lncRNAs in gastric cancer.BMC Cancer. 2022 Mar 24;22(1):316. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09377-8. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35331183 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological implications of lncRNAs, immunotherapy and DNA methylation in lung squamous cell carcinoma: a narrative review.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 Dec;10(12):5406-5429. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-1607. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35116387 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor microenvironment characteristics and prognostic role of m6A modification in lung squamous cell carcinoma.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 28;10(5):e26851. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26851. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38455573 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNA-Mediated N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) deposition: A pivotal regulator of cancer, impacting key signaling pathways in carcinogenesis and therapy response.Noncoding RNA Res. 2023 Nov 13;9(1):84-104. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2023.11.005. eCollection 2024 Mar. Noncoding RNA Res. 2023. PMID: 38075202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
m6A-Related lncRNAs Are Potential Prognostic Biomarkers of Cervical Cancer and Affect Immune Infiltration.Dis Markers. 2022 Apr 11;2022:8700372. doi: 10.1155/2022/8700372. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35432630 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic and therapeutic insights into the function of N6-methyladenosine in arthritic diseases.Inflamm Res. 2025 Jan 7;74(1):7. doi: 10.1007/s00011-024-01969-3. Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 39762508 Review.
-
The lncRNA epigenetics: The significance of m6A and m5C lncRNA modifications in cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 9;13:1063636. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1063636. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36969033 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

