Gut-Bone Axis: A Non-Negligible Contributor to Periodontitis
- PMID: 34869062
- PMCID: PMC8637199
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.752708
Gut-Bone Axis: A Non-Negligible Contributor to Periodontitis
Abstract
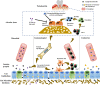
Periodontitis is a polymicrobial infectious disease characterized by alveolar bone loss. Systemic diseases or local infections, such as diabetes, postmenopausal osteoporosis, obesity, and inflammatory bowel disease, promote the development and progression of periodontitis. Accumulating evidences have revealed the pivotal effects of gut microbiota on bone health via gut-alveolar-bone axis. Gut pathogens or metabolites may translocate to distant alveolar bone via circulation and regulate bone homeostasis. In addition, gut pathogens can induce aberrant gut immune responses and subsequent homing of immunocytes to distant organs, contributing to pathological bone loss. Gut microbial translocation also enhances systemic inflammation and induces trained myelopoiesis in the bone marrow, which potentially aggravates periodontitis. Furthermore, gut microbiota possibly affects bone health via regulating the production of hormone or hormone-like substances. In this review, we discussed the links between gut microbiota and periodontitis, with a particular focus on the underlying mechanisms of gut-bone axis by which systemic diseases or local infections contribute to the pathogenesis of periodontitis.
Keywords: alveolar bone loss; gut epithelial barrier; gut microbiota; gut-bone axis; osteoimmunology; periodontitis.
Copyright © 2021 Jia, Yang, Li, Zhao, Zhou and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aimetti M., Perotto S., Castiglione A., Mariani G. M., Ferrarotti F., Romano F. (2015). Prevalence of Periodontitis in an Adult Population From an Urban Area in North Italy: Findings From a Cross-Sectional Population-Based Epidemiological Survey. J. Clin. Periodontol. 42 (7), 622–631. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12420 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

