Case Report: Bullous Lung Disease Following COVID-19
- PMID: 34869488
- PMCID: PMC8635639
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.770778
Case Report: Bullous Lung Disease Following COVID-19
Abstract
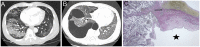
More than 87% of patients report the persistence of at least one symptom after recovery from the Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Dyspnea is one of the most frequently reported symptoms following severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS CoV-2) infection with persistent chest radiological abnormalities up to 3 months after symptom onset. These radiological abnormalities are variable and most commonly include ground-glass opacities, reticulations, mosaic attenuation, parenchymal bands, interlobular septal thickening, bronchiectasis, and fibrotic-like changes. However, in this case report, we describe findings of bullous lung disease as a complication of SARS CoV-2 infection. As the pandemic continues, there is a need to understand the multiple respiratory manifestations of post-acute sequelae of COVID-19. We, therefore, present this case to add to the current body of literature describing pulmonary disease as a consequence of SARS CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS CoV-2; bullous lung disease; post-COVID “Long Haulers”; post-acute COVID-19.
Copyright © 2021 Pednekar, Amoah, Homer, Ryu and Lutchmansingh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Guler SA, Ebner L, Aubry-Beigelman C, Bridevaux PO, Brutsche M, Clarenbach C, et al. . Pulmonary function and radiological features 4 months after COVID-19: first results from the national prospective observational Swiss COVID-19 lung study. Eur Respir J. (2021) 57:2003690. 10.1183/13993003.03690-2020 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

