Intracellular Staphylococcus aureus Infection Decreases Milk Protein Synthesis by Preventing Amino Acid Uptake in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells
- PMID: 34869729
- PMCID: PMC8636274
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2021.756375
Intracellular Staphylococcus aureus Infection Decreases Milk Protein Synthesis by Preventing Amino Acid Uptake in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells
Abstract
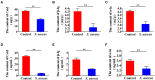
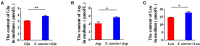
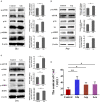
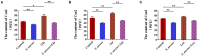
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is one of the main pathogens in cow mastitis, colonizing mammary tissues and being internalized into mammary epithelial cells, causing intracellular infection in the udder. Milk that is produced by cows that suffer from mastitis due to S. aureus is associated with decreased production and changes in protein composition. However, there is limited information on how mastitis-inducing bacteria affect raw milk, particularly with regard to protein content and protein composition. The main purpose of this work was to examine how S. aureus infection affects milk protein synthesis in bovine mammary epithelial cells (BMECs). BMECs were infected with S. aureus, and milk protein and amino acid levels were determined by ELISA after S. aureus invasion. The activity of mTORC1 signaling and the transcription factors NF-κB and STAT5 and the expression of the amino acid transporters SLC1A3 and SLC7A5 were measured by western blot or immunofluorescence and RT-qPCR. S. aureus was internalized by BMECs in vitro, and the internalized bacteria underwent intracellular proliferation. Eight hours after S. aureus invasion, milk proteins were downregulated, and the level of BMECs that absorbed Glu, Asp, and Leu from the culture medium and the exogenous amino acids induced β-casein synthesis declined. Further, the activity of mTORC1 signaling, NF-κB, and STAT5 was impaired, and SLC1A3 and SLC7A5 were downregulated. Eight hours of treatment with 100 nM rapamycin inhibited NF-κB and STAT5 activity, SLC1A3 and SLC7A5 expression, and milk protein synthesis in BMECs. Thus mTORC1 regulates the expression of SLC1A3 and SLC7A5 through NF-κB and STAT5. These findings constitute a model by which S. aureus infection suppresses milk protein synthesis by decreasing amino acids uptake in BMECs.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; amino acid; amino acid transporters; bovine mammary epithelial cells; mTORC1; milk protein synthesis.
Copyright © 2021 Chen, Ma, Ji, Yang, Feng, Yao, Cheng, Li, Wang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

