Effects of Ozone on Hippocampus BDNF and Fos Expressions in Rats with Chronic Compression of Dorsal Root Ganglia
- PMID: 34869766
- PMCID: PMC8642004
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5572915
Effects of Ozone on Hippocampus BDNF and Fos Expressions in Rats with Chronic Compression of Dorsal Root Ganglia
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Effects of Ozone on Hippocampus BDNF and Fos Expressions in Rats with Chronic Compression of Dorsal Root Ganglia.Biomed Res Int. 2024 Mar 20;2024:9821958. doi: 10.1155/2024/9821958. eCollection 2024. Biomed Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38549992 Free PMC article.
Abstract
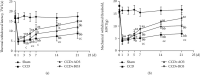
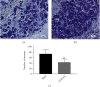
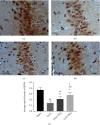
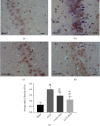
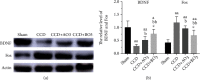
The effects of ozone on hippocampal expression levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and c-fos protein (Fos) were evaluated in rats with chronic compression of dorsal root ganglia (CCD). Forty-eight adult female Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into the following 4 groups (n = 12): sham operation (sham group), CCD group, CCD with 20 μg/ml of ozone (CCD + AO3 group), and CCD with 40 μg/ml of ozone (CCD + BO3 group). Except the sham group, unilateral L5 dorsal root ganglion (DRG) compression was performed on all other groups. On days 1, 2, and 4 after the operation, the CCD + AO3 and CCD + BO3 groups were injected with 100 μl of ozone with concentrations of 20 and 40 μg/ml, respectively. Thermal withdrawal latencies (TWLs) and mechanical withdrawal thresholds (MWTs) were measured at various time points before and after the operation. BDNF and Fos expressions were examined in the extracted hippocampi using immunohistochemistry. The TWLs and MWTs of CCD model rats that received ozone were lower with decreased BDNF and increased Fos expression levels, on day 21 after the operation, compared to those of the sham group (P < 0.05). The TWLs and MWTs of the CCD + AO3 and CCD + BO3 groups were higher with increased BDNF and decreased Fos expression levels, on day 21 after the operation, compared to those of the CCD group (P < 0.05). The TWLs were longer and the MWTs were higher in the CCD + BO3 group at each time point with increased BDNF and decreased Fos expression levels, on day 21 after the operation, compared to those of the CCD + AO3 group (P < 0.05). Our results revealed that ozone can relieve the neuropathic pain caused by the pathological neuralgia resulting from DRG compression in rats. The mechanism of action for ozone is likely associated with changes in BDNF and Fos expression levels in the hippocampus.
Copyright © 2021 Lingling Zhu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

