The role of the Nrf2/Keap1 signaling cascade in mechanobiology and bone health
- PMID: 34869801
- PMCID: PMC8626578
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bonr.2021.101149
The role of the Nrf2/Keap1 signaling cascade in mechanobiology and bone health
Abstract
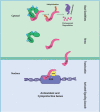
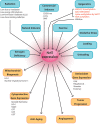
In conjunction with advancements in modern medicine, bone health is becoming an increasingly prevalent concern among a global population with an ever-growing life expectancy. Countless factors contribute to declining bone strength, and age exacerbates nearly all of them. The detrimental effects of bone loss have a profound impact on quality of life. As such, there is a great need for full exploration of potential therapeutic targets that may provide antiaging benefits and increase the life and strength of bone tissues. The Keap1-Nrf2 pathway is a promising avenue of this research. The cytoprotective and antioxidant functions of this pathway have been shown to mitigate the deleterious effects of oxidative stress on bone tissues, but the exact cellular and molecular mechanisms by which this occurs are not yet fully understood. Presently, refined animal and loading models are allowing exploration into the effect of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in a tissue-specific or even cell-specific manner. In addition, Nrf2 activators currently undergoing clinical trials can be utilized to investigate the particular cellular mechanisms at work in this cytoprotective cascade. Although the timing and dosing of treatment with Nrf2 activators need to be further investigated, these activators have great potential to be used clinically to prevent and treat osteoporosis.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Keap1; Mechanobiology; Nrf2; Osteoporosis.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Alam J., et al. Nrf2, a Cap'n'Collar transcription factor, regulates induction of the heme oxygenase-1 gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:26071. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

