Direct Interstitial Decongestion in an Animal Model of Acute-on-Chronic Ischemic Heart Failure
- PMID: 34869951
- PMCID: PMC8617571
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2021.09.008
Direct Interstitial Decongestion in an Animal Model of Acute-on-Chronic Ischemic Heart Failure
Abstract
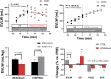
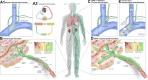
Removal of excess fluid in acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) targets the intravascular space, whereas most fluid resides in the interstitial space. The authors evaluated an approach to interstitial decongestion using a device to enhance lymph flow. The device was deployed in sheep with induced heart failure (HF) and acute volume overload to create a low-pressure zone at the thoracic duct outlet. Treatment decreased extravascular lung water (EVLW) volume (mL/kg) (-32% ± 9%, P = 0.029) compared to controls (+46% ± 9%, P = 0.003). Device-mediated thoracic duct decompression effectively reduced EVLW. Human studies may establish device-based interstitial decongestion as a new ADHF treatment.
Keywords: ADHF, acute decompensated heart failure; CVP, central venous pressure; EVLW, extravascular lung water; acute decompensated heart failure; decongestion; interstitial; lymphatic; pulmonary edema; thoracic duct; volume overload.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
WhiteSwell funded the studies. Drs Abraham, Jonas, and Dongaonkar have received consulting fees from WhiteSwell. Drs Geist, Ueyama, Render, Youngblood, Muir, Hamlin, and del Rio have received research fees from WhiteSwell for the conduct of the animal studies.
Figures



References
-
- Hollenberg S.M., Warner Stevenson L., Ahmad T., et al. 2019 ACC expert consensus decision pathway on risk assessment, management, and clinical trajectory of patients hospitalized with heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:1966–2011. - PubMed
-
- Harjola V.P., Parissis J., Brunner-La Rocca H.P., et al. Comprehensive in-hospital monitoring in acute heart failure: applications for clinical practice and future directions for research. A statement from the Acute Heart Failure Committee of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur J Heart Fail. 2018;20:1081–1099. - PubMed
-
- Lala A., McNulty S.E., Mentz R.J., et al. Relief and recurrence of congestion during and after hospitalization for acute heart failure: insights from Diuretic Optimization Strategy Evaluation in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (DOSE-AHF) and Cardiorenal Rescue Study in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (CARESS-HF) Circ Heart Fail. 2015;8:741–748. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fudim M., Loungani R., Doerfler S.M., et al. Worsening renal function during decongestion among patients hospitalized for heart failure: findings from the Evaluation Study of Congestive Heart Failure and Pulmonary Artery Catheterization Effectiveness (ESCAPE) trial. Am Heart J. 2018;204:163–173. - PubMed
-
- Bensimhon D., Alali S.A., Curran L., et al. The use of the reds noninvasive lung fluid monitoring system to assess readiness for discharge in patients hospitalized with acute heart failure: a pilot study. Heart Lung. 2021;50:59–64. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

