Comprehensive literature review on COVID-19 vaccines and role of SARS-CoV-2 variants in the pandemic
- PMID: 34870090
- PMCID: PMC8637774
- DOI: 10.1177/25151355211059791
Comprehensive literature review on COVID-19 vaccines and role of SARS-CoV-2 variants in the pandemic
Abstract
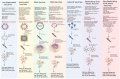
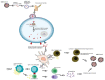
Since the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been a rapid expansion in vaccine research focusing on exploiting the novel discoveries on the pathophysiology, genomics, and molecular biology of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. Although the current preventive measures are primarily socially distancing by maintaining a 1 m distance, it is supplemented using facial masks and other personal hygiene measures. However, the induction of vaccines as primary prevention is crucial to eradicating the disease to attempt restoration to normalcy. This literature review aims to describe the physiology of the vaccines and how the spike protein is used as a target to elicit an antibody-dependent immune response in humans. Furthermore, the overview, dosing strategies, efficacy, and side effects will be discussed for the notable vaccines: BioNTech/Pfizer, Moderna, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Gamaleya, and SinoVac. In addition, the development of other prominent COVID-19 vaccines will be highlighted alongside the sustainability of the vaccine-mediated immune response and current contraindications. As the research is rapidly expanding, we have looked at the association between pregnancy and COVID-19 vaccinations, in addition to the current reviews on the mixing of vaccines. Finally, the prominent emerging variants of concern are described, and the efficacy of the notable vaccines toward these variants has been summarized.
Keywords: AstraZeneca; BioNTech/Pfizer; COVID-19 vaccine; Moderna; SARS-CoV-2 variants.
© The Author(s), 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Johns Hopkins University & Medicine. COVID-19 dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU). Coronavirus Resource Center, Johns Hopkins University & Medicine, 2021, https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html
-
- McCormick LC, Benhamou M, Pogkas D. The Covid-19 pandemic has added $19.5 trillion to global debt. Bloomberg, 27 January 2021, https://www.bloomberg.com/graphics/2021-coronavirus-global-debt/#:~:text...
-
- WHO. COVID-19 vaccine tracker and landscape, 2021, https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/draft-landscape-of-covid-19-cand...
-
- Krammer F. SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in development. Nature 2020; 586(7830): 516–527. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

