Assessment of High Risk for Alzheimer's Disease Using Plasma Biomarkers in Subjects with Normal Cognition in Taiwan: A Preliminary Study
- PMID: 34870102
- PMCID: PMC8609520
- DOI: 10.3233/ADR-210310
Assessment of High Risk for Alzheimer's Disease Using Plasma Biomarkers in Subjects with Normal Cognition in Taiwan: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
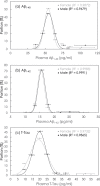
Background: In Alzheimer's disease (AD), cognitive impairment begins 10-15 years later than neurodegeneration in the brain. Plasma biomarkers are promising candidates for assessing neurodegeneration in people with normal cognition. It has been reported that subjects with the concentration of plasma amyloid-β 1-42×total tau protein higher than 455 pg2/ml2 are assessed as having a high risk of amnesic mild impairment or AD, denoted as high risk of AD (HRAD).
Objective: The prevalence of high-risk for dementia in cognitively normal controls is explored by assaying plasma biomarkers.
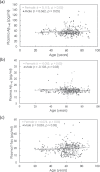
Methods: 422 subjects with normal cognition were enrolled around Taiwan. Plasma Aβ1-40, Aβ1-42, and T-Tau levels were assayed using immunomagnetic reduction to assess the risk of dementia.
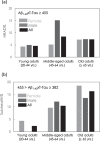
Results: The results showed that 4.6% of young adults (age: 20-44 years), 8.5% of middle-aged adults (age: 45-64 years), and 7.3% of elderly adults (age: 65-90 years) had HRAD. The percentage of individuals with HRAD dramatically increased in middle-aged and elderly adults compared to young adults.
Conclusion: The percentage of HRAD in cognitively normal subjects are approximately 10%, which reveals that the potentially public-health problem of AD in normal population. Although the subject having abnormal levels of Aβ or tau is not definitely going on to develop cognitive declines or AD, the risk of suffering cognitive impairment in future is relatively high. Suitable managements are suggested for these high-risk cognitively normal population. Worth noting, attention should be paid to preventing cognitive impairment due to AD, not only in elderly adults but also middle-aged adults.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; immunomagnetic reduction; normal cognition; plasma biomarkers.
© 2021 – IOS Press. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
SY Yang is an employee and a shareholder of MagQu Co., Ltd. Other authors do not have conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Liu HC, Lin KN, Teng EL, Wang SJ, Fuh JL, Guo NW, Chou P, Hu HH, Chiang BN (1995) Prevalence and subtypes of dementia in Taiwan: A community survey of 5297 individuals. J Am Geriatr Soc 43, 144–149. - PubMed
-
- Fuh JL, Wang SJ (2008) Dementia in Taiwan: Past, present, and future. Acta Neurol Taiwan 17, 153–161. - PubMed
-
- McKhann GM, Knopman DS, Chertkow H, Hyman BT, Jack CR Jr., Kawas CH, Klunk WE, Koroshetz WJ, Manly JJ, Mayeux R, Mohs RC, Morris JC, Rossor MN, Scheltens P, Carrillo MC, Thies B, Weintraub S, Phelps CH (2011) The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 7, 263–269. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

