Metabolic causes and consequences of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- PMID: 34870138
- PMCID: PMC8626571
- DOI: 10.1016/j.metop.2021.100149
Metabolic causes and consequences of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding previously published articles.Metabol Open. 2023 Jan 21;17:100231. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2023.100231. eCollection 2023 Mar. Metabol Open. 2023. PMID: 36992679 Free PMC article.
Abstract
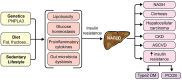
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a multifactorial metabolic disorder that was first described in 1980. It has been prevalent and on the rise for many years and is associated with other metabolic disorders such as obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). NAFLD can be best described as a metabolic dysfunction that stems from insulin resistance-induced hepatic lipogenesis. This lipogenesis increases oxidative stress and hepatic inflammation and is often potentiated by genetic and gut microbiome dysfunction. As NAFLD progresses from simple steatosis to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the odds of complications including cardiovascular disease (CVD), chronic kidney disease (CKD), and overall mortality increase. The aim of this review is to describe the metabolic causes and consequences of NAFLD while examining the risks that each stage of NAFLD poses. In this review, the etiology of "lean" NAFLD, the impact of obesity, T2DM, genetics, and microbiome dysbiosis on NAFLD progression are all explored. This review will also discuss the core issue behind the progression of NAFLD: insulin resistance (IR). Upon describing the causes and consequences of NAFLD, the effectiveness of diet modification, lifestyle changes, and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP-1) agonists to retard NAFLD progression and stem the rate of complications is examined.
© 2021 Northwell Health.
Figures
References
-
- Ludwig J., Viggiano T.R., McGill D.B., Oh B.J. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 1980;55(7):434–438. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

