Can the application of graphene oxide contribute to the fight against COVID-19? Antiviral activity, diagnosis and prevention
- PMID: 34870157
- PMCID: PMC8491929
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crphar.2021.100062
Can the application of graphene oxide contribute to the fight against COVID-19? Antiviral activity, diagnosis and prevention
Abstract
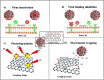
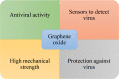
COVID-19 is an infectious disease that affects the respiratory system and is caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. It was first reported in Wuhan, China, on December 31, 2019, and has affected the entire world. This pandemic has caused serious health, economic and social problems. In this situation, the only solution to combat COVID-19 is to accelerate the development of antiviral drugs and vaccines to mitigate the virus and develop better antiviral methods and excellent diagnostic and prevention techniques. With the development of nanotechnology, nanoparticles are being introduced to control COVID-19. Graphene oxide (GO), an oxidized derivative of graphene, is currently used in the medical field to treat certain diseases such as cancer. It is characterized by very important antiviral properties that allow its use in treating certain infectious diseases. The GO antiviral mechanism is discussed by the virus inactivation and/or the host cell receptor or by the physicochemical destruction of viral species. Moreover, the very high surface/volume ratio of GO allows the fixation of biomolecules by simple absorption. This paper summarizes the different studies performed on GO's antiviral activities and discusses GO-based biosensors for virus detection and approaches for prevention.
Keywords: Antiviral activity; Biosensors; COVID-19; Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2; Detection; Graphene oxide; Pandemic; Prevention.
© 2021 Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Can nanotechnology help in the fight against COVID-19?Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2020 Sep;18(9):849-864. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2020.1776115. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2020. PMID: 32574081 Review.
-
Antiviral potential of nanoparticles for the treatment of Coronavirus infections.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2022 Jul;72:126977. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2022.126977. Epub 2022 Mar 26. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35397331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potentialities of graphene and its allied derivatives to combat against SARS-CoV-2 infection.Mater Today Adv. 2022 Mar;13:100208. doi: 10.1016/j.mtadv.2022.100208. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Mater Today Adv. 2022. PMID: 35039802 Free PMC article.
-
Current Strategies of Antiviral Drug Discovery for COVID-19.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 13;8:671263. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.671263. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34055887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of nanotechnology in combating coronavirus.3 Biotech. 2021 Jul;11(7):358. doi: 10.1007/s13205-021-02905-6. Epub 2021 Jun 28. 3 Biotech. 2021. PMID: 34221822 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
COVID-19 therapy, from lung disease to systemic disorder.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022;3:100099. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100099. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 35382154 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Graphene oxide nanoparticles inhibit H9N2 influenza A virus infectivity by destroying viral coat proteins.Arch Virol. 2024 Sep 3;169(9):192. doi: 10.1007/s00705-024-06117-0. Arch Virol. 2024. PMID: 39225747
-
Carbon-based nanomaterials against SARS-CoV-2: Therapeutic and diagnostic applications.OpenNano. 2023 Mar;10:100121. doi: 10.1016/j.onano.2023.100121. Epub 2023 Feb 18. OpenNano. 2023. PMID: 40478147 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation interaction of graphene oxide with heparin for antiviral blockade: a study of ab initio simulations, molecular docking, and experimental analysis.J Mol Model. 2023 Jul 7;29(8):235. doi: 10.1007/s00894-023-05645-x. J Mol Model. 2023. PMID: 37418181
-
Molecular interactions of the Omicron, Kappa, and Delta SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins with quantum dots of graphene oxide.J Mol Model. 2024 Jun 11;30(7):203. doi: 10.1007/s00894-024-05996-z. J Mol Model. 2024. PMID: 38858279
References
-
- Alayande A.B., Chae S., et al. Kim I.S. « Surface morphology-dependent spontaneous bacterial behaviors on graphene oxide membranes ». Separ. Purif. Technol. 2019;226:68–74.
-
- Afroj S., Tan S., Abdelkader A., Novoselov K., et al. Karim N. « highly conductive, scalable, and machine washable graphene-based E-textiles for multifunctional wearable electronic applications ». Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020;30:2000293. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202000293. avr. - DOI
-
- Akhavan O., Choobtashani M., Ghaderi et E. « protein degradation and RNA efflux of viruses photocatalyzed by graphene–tungsten oxide composite under visible light irradiation ». J. Phys. Chem. C. 2012;116(17):9653–9659. doi: 10.1021/jp301707m. mai. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

