Maternal Obsessive-Compulsive Symptoms and Infant Feeding Practices
- PMID: 34870468
- PMCID: PMC8972019
- DOI: 10.1089/bfm.2021.0062
Maternal Obsessive-Compulsive Symptoms and Infant Feeding Practices
Abstract
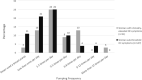
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to examine associations between postpartum obsessive-compulsive (OC) symptoms, infant care and feeding worries, and breastfeeding experiences in a sample of postpartum women. Materials and Methods: Women were recruited via an online U.S. research volunteer database and were eligible if they were aged 18-47 years, their primary language was English, they had an infant 2-6 months old, and tried breastfeeding the infant at least once. Participants completed a survey to assess breastfeeding experiences and practices, OC symptoms and other mental health conditions, and demographics. Modified Poisson regression and linear regression were used to estimate associations between clinically elevated OC symptoms, reported thoughts or worries about infant feeding and care, and breastfeeding experiences, problems, and duration. Results: Of 232 participants, 32 (14%) had clinically elevated OC symptoms. These women had more perinatal OC symptoms (scoring 3.6 points higher on perinatal OC symptoms score [95% confidence interval {CI}: 0.4 to 6.9]), including symptoms specific to infant care and feeding [e.g., adjusted relative risk(repeated washing of baby's bottles, bowl, or plate) = 2.37, 95% CI:1.55 to 3.64], and more breastfeeding problems (adjusted β = 0.3, 95% CI: 0.0 to 0.2) than women with fewer OC symptoms. However, they did not report an overall worse breastfeeding experience (adjusted β = 0.4, 95% CI: -9.3 to 10.1). Adjusted models controlled for depressive symptoms. Conclusions: Obsessive thoughts and compulsions were common in this sample and extended to infant feeding activities. These symptoms were associated with more breastfeeding problems. Interactions in mother-infant dyads are critical because of lasting impacts on parent-child relationships and child development. Treating OC symptoms may foster healthier mother-infant relationships.
Keywords: anxiety; breastfeeding; obsessive-compulsive disorder; postpartum.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (APA). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association (APA), 2013.
-
- Navarro P, García-Esteve L, Ascaso C, et al. . Non-psychotic psychiatric disorders after childbirth: Prevalence and comorbidity in a community sample. J Affect Disord 2008;109:171–176. - PubMed
-
- Wenzel A, Haugen EN, Jackson LC, et al. . Anxiety symptoms and disorders at eight weeks postpartum. J Anxiety Disord 2005;19:295–311. - PubMed
-
- Sadock BJ, Kaplan HI, Sadock VA. Kaplan and Sadock's Synopsis of Psychiatry: Behavioral Sciences/Clinical Psychiatry, 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

