Serum and urinary biomarkers for early detection of acute kidney injury following Hypnale spp. envenoming
- PMID: 34871314
- PMCID: PMC8675918
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010011
Serum and urinary biomarkers for early detection of acute kidney injury following Hypnale spp. envenoming
Abstract
Background: Hump-nosed pit viper (HNV; Hypnale spp.) bites account for most venomous snakebites in Sri Lanka. Acute kidney injury (AKI) is the most serious systemic manifestation (1-10%) following HNV envenoming. We aimed to identify the value of functional and injury biomarkers in predicting the development of AKI early following HNV bites.
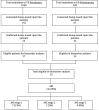
Methods: We conducted a prospective cohort study of patients with confirmed HNV envenoming presenting to two large tertiary care hospitals in Sri Lanka. Demographics, bite details, clinical effects, complications and treatment data were collected prospectively. Blood and urine samples were collected from patients for coagulation and renal biomarker assays on admission, at 0-4h, 4-8h, 8-16h and 16-24h post-bite and daily until discharge. Follow-up samples were obtained 1 and 3 months post-discharge. Creatinine (sCr) and Cystatin C (sCysC) were measured in serum and kidney injury molecule-1 (uKIM-1), clusterin (uClu), albumin (uAlb), β2-microglobulin (uβ2M), cystatin C (uCysC), neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (uNGAL), osteopontin (uOPN) and trefoil factor-3 (uTFF-3) were measured in urine. Definite HNV bites were based on serum venom specific enzyme immunoassay. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) criteria were used to stage AKI. Two patients had chronic kidney disease at 3 month follow-up, both with pre-existing abnormal sCr, and one developed AKI following HNV envenoming.
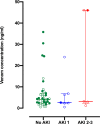
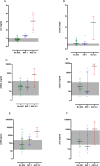
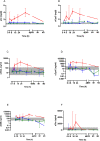
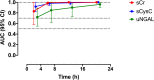
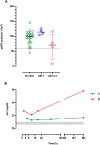
Results: There were 52 patients with confirmed HNV envenoming; median age 48y (Interquartile range [IQR]:40-59y) and 29 (56%) were male. Median time to admission was 1.87h (IQR:1-2.75h). Twelve patients (23%) developed AKI (AKI stage 1 = 7, AKI stage 2 = 1, AKI stage 3 = 4). Levels of five novel biomarkers, the functional marker serum Cystatin C and the damage markers urinary NGAL, cystatin C, β2-microglobulin and clusterin, were elevated in patients who developed moderate/severe acute kidney injury. sCysC performed the best at 0-4 h post-bite in predicting moderate to severe AKI (AUC-ROC 0.95;95%CI:0.85-1.0) and no biomarker performed better than sCr at later time points.
Conclusions: sCysC appears to be a better marker than sCr for early prediction of moderate to severe AKI following HNV envenoming.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early identification of acute kidney injury in Russell's viper (Daboia russelii) envenoming using renal biomarkers.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Jul 1;13(7):e0007486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007486. eCollection 2019 Jul. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 31260445 Free PMC article.
-
Severe acute kidney injury following Sri Lankan Hypnale spp. envenoming is associated with thrombotic microangiopathy.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2021 Apr;59(4):296-302. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2020.1810695. Epub 2020 Sep 1. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2021. PMID: 32870056
-
Kidney injury following envenoming by hump-nosed pit viper (Genus: Hypnale) in Sri Lanka: proven and probable cases.Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2019 Mar 1;113(3):131-142. doi: 10.1093/trstmh/try120. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2019. PMID: 30544230
-
Biomarkers of renal function, which and when?Clin Chim Acta. 2015 Jan 1;438:350-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2014.08.039. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Clin Chim Acta. 2015. PMID: 25195004 Review.
-
Hypnale coagulopathy: snake envenomation of a different kind.J R Coll Physicians Edinb. 2021 Mar;51(1):31-36. doi: 10.4997/JRCPE.2021.108. J R Coll Physicians Edinb. 2021. PMID: 33877131 Review.
Cited by
-
The clusterin connectome: Emerging players in chondrocyte biology and putative exploratory biomarkers of osteoarthritis.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 15;14:1103097. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1103097. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37033956 Free PMC article.
-
Snakebite Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy and Recommendations for Clinical Practice.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Jan 14;14(1):57. doi: 10.3390/toxins14010057. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35051033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical characteristics of snake envenomation-related acute kidney injury in South Korea.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 8;14(1):23503. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74142-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39379492 Free PMC article.
-
New triple therapy for the diagnosis of CKD-MBD: a cross-sectional study in Shanxi province.BMJ Open. 2024 Aug 17;14(8):e081485. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-081485. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39153776 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

