Unmet need for family planning and associated factors among currently married women of reproductive age in Bishoftu town, Eastern Ethiopia
- PMID: 34871318
- PMCID: PMC8648111
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260972
Unmet need for family planning and associated factors among currently married women of reproductive age in Bishoftu town, Eastern Ethiopia
Abstract
Background: Unmet family planning is one of the common causes for low contraceptive prevalence rates in developing countries, including Ethiopia. Rapid urbanization had profound effect on population health, however, little is known about the unmet need of family planning in settings where there was increased industrializations and internal migrations in Ethiopia. This study aims to determine the unmet need for family planning services among currently married women and identify factors associated with it in Bishoftu town, Eastern Ethiopia.
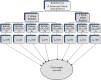
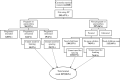
Methods: Community-based cross-sectional study was conducted from 1st January to 28th February, 2021 among 847 randomly sampled currently married women of the reproductive age group. Data were collected using semi structured interviewer administered questionnaire. Multivariate logistic regression was used to identify factors associated with the outcome variable and a 95% confidence interval was used to declare the presence of statistical significance associations.
Results: Eight hundred twenty-eight women were participated in the study. The prevalence of unmet need for family planning among currently married women was 26% [95% CI: 23,29]. Maternal age [AOR, 3.00, 95% CI:1.51-5.95], educational status [AOR, 2.49, 95% CI:1.22-5.07], occupational status of self-employee [AOR, 1.98, 95% CI:1.15-3.39] and housewife [AOR, 1.78, 95% CI:1.02-3.12], being visited by health care provider in the last 12 months [AOR, 1.81, 95% CI: 1.26-2.60] and desired number of children less than two [AOR, 1.53, 95% CI:1.01-2.30] were significantly associated with unmet need for family planning.
Conclusions: Unmet need for family planning was higher in the study area compared with the United Nations sphere standard of unmet need for family planning and the national average, and slightly lower than the regional average. Socio-demographic, economic, and health institution factors were determinants of the unmet need for family planning in the study area. Therefore, health education and behaviour change communication related to family planning services should be strengthened and access to family planning services should be improved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Eight out of every twenty-five married women have an unmet need for family planning in Meyu Muluke District, Eastern Ethiopia.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 21;15(1):13761. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-91297-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40258850 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of unmet need for contraceptive method among young married women in Ethiopia: Multilevel analysis of Ethiopia Demographic and Health Survey 2016.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 5;19(9):e0306068. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306068. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39236003 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and factors associated with unmet need for family planning among the currently married reproductive age women in Shire-Enda- Slassie, Northern West of Tigray, Ethiopia 2015: a community based cross-sectional study.Pan Afr Med J. 2016 Apr 15;23:195. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2016.23.195.8386. eCollection 2016. Pan Afr Med J. 2016. PMID: 27347284 Free PMC article.
-
Magnitude and associated factors of unmet need for family planning among reproductive-aged women in Ethiopia: An umbrella review.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 1;19(8):e0308085. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308085. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39088583 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and determinants of the involvement of married men in family planning services in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Womens Health (Lond). 2022 Jan-Dec;18:17455057221099083. doi: 10.1177/17455057221099083. Womens Health (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35593087 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A narrative review of evidence to support increased domestic resource mobilization for family planning in Nigeria.BMC Womens Health. 2023 May 6;23(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s12905-023-02396-y. BMC Womens Health. 2023. PMID: 37149568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unmet need for family planning and associated factors among reproductive age women working in Bole Lemi industrial park, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia 2024: an institution based cross-sectional study.BMC Public Health. 2025 Jun 4;25(1):2082. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-23327-6. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40468234 Free PMC article.
-
Magnitude of unmet need for family planning and associated factors among women in the extended postpartum period in Dabat district, Northwest Ethiopia. evidence from Dabat demographic health surveys.BMC Public Health. 2023 Jun 12;23(1):1123. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16046-3. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37308903 Free PMC article.
-
Unmet need for family planning and associated factors among currently married women in Hawella Tulla subcity, Hawassa, southern Ethiopia: community-based study.Contracept Reprod Med. 2023 Feb 10;8(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s40834-022-00212-w. Contracept Reprod Med. 2023. PMID: 36759856 Free PMC article.
-
Client-centered counseling and facilitation in improving modern contraceptive uptake in urban slum of Karachi Pakistan.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 31;18(7):e0289107. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0289107. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37523392 Free PMC article.
References
-
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2014).World Contraceptive Use 2014 (POP/DB/CP/Rev2014). 2014. p. 1–3.
-
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs PD. World Fertility and Family Planning 2020: Highlights (ST/ESA/SER.A/440). World Fertility and Family Planning 2020: Highlights. 2020.
-
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division. Estimates and Projections of Family Planning Indicators 2019. Available from:https://www.un.org/development/desa/pd/content/family-planning-and-2030-.... 2020.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical