An automated radiosynthesis of [18F]DPA-714 on a commercially available radiosynthesizer, Elixys Flex/Chem
- PMID: 34871885
- PMCID: PMC8858596
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2021.110032
An automated radiosynthesis of [18F]DPA-714 on a commercially available radiosynthesizer, Elixys Flex/Chem
Abstract
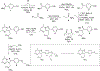
[18F]DPA-714 is a radiotracer specific to the translocator protein (TSPO) and is useful for in vivo Positron Emission Tomography imaging studies. In this report, we have developed an automated radiosynthesis of [18F]DPA-714 on a commercially-available radiosynthesis platform, which comports with USP <823> guidelines. The wide availability of the radiosynthesis module and ease of dissemination of the production sequence will facilitate preclinical and clinical research of TSPO-related pathology.
Keywords: Automation; F-18; Fluorine-18; Positron emission tomography; Radiochemistry; Radiosynthesis.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
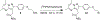
References
-
- Arlicot N, Vercouillie J, Ribeiro M-J, Tauber C, Venel Y, Baulieu J-L, Maia S, Corcia P, Stabin MG, Reynolds A, Kassiou M, & Guilloteau D (2012). Initial evaluation in healthy humans of [18F]DPA-714, a potential PET biomarker for neuroinflammation. Nuclear Medicine and Biology, 39(4), 570–578. 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2011.10.012 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Banister SD, Wilkinson SM, Hanani R, Reynolds AJ, Hibbs DE, & Kassiou M (2012). A practical, multigram synthesis of the 2-(2-(4-alkoxyphenyl)-5,7-dimethylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)acetamide (DPA) class of high affinity translocator protein (TSPO) ligands. Tetrahedron Letters, 53(29), 3780–3783. 10.1016/j.tetlet.2012.05.044 - DOI
-
- Chauveau F, Camp NV, Dollé F, Kuhnast B, Hinnen F, Damont A, Boutin H, James M, Kassiou M, & Tavitian B (2009). Comparative Evaluation of the Translocator Protein Radioligands 11C-DPA-713, 18F-DPA-714, and 11C-PK11195 in a Rat Model of Acute Neuroinflammation. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 50(3), 468–476. 10.2967/jnumed.108.058669 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

