Prognostication using SpO2/FiO2 in invasively ventilated ICU patients with ARDS due to COVID-19 - Insights from the PRoVENT-COVID study
- PMID: 34872014
- PMCID: PMC8641962
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2021.11.009
Prognostication using SpO2/FiO2 in invasively ventilated ICU patients with ARDS due to COVID-19 - Insights from the PRoVENT-COVID study
Abstract
Background: The SpO2/FiO2 is a useful oxygenation parameter with prognostic capacity in patients with ARDS. We investigated the prognostic capacity of SpO2/FiO2 for mortality in patients with ARDS due to COVID-19.
Methods: This was a post-hoc analysis of a national multicenter cohort study in invasively ventilated patients with ARDS due to COVID-19. The primary endpoint was 28-day mortality.
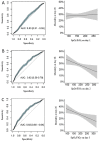
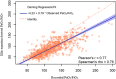
Results: In 869 invasively ventilated patients, 28-day mortality was 30.1%. The SpO2/FiO2 on day 1 had no prognostic value. The SpO2/FiO2 on day 2 and day 3 had prognostic capacity for death, with the best cut-offs being 179 and 199, respectively. Both SpO2/FiO2 on day 2 (OR, 0.66 [95%-CI 0.46-0.96]) and on day 3 (OR, 0.70 [95%-CI 0.51-0.96]) were associated with 28-day mortality in a model corrected for age, pH, lactate levels and kidney dysfunction (AUROC 0.78 [0.76-0.79]). The measured PaO2/FiO2 and the PaO2/FiO2 calculated from SpO2/FiO2 were strongly correlated (Spearman's r = 0.79).
Conclusions: In this cohort of patients with ARDS due to COVID-19, the SpO2/FiO2 on day 2 and day 3 are independently associated with and have prognostic capacity for 28-day mortality. The SpO2/FiO2 is a useful metric for risk stratification in invasively ventilated COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: Acute respiratory distress syndrome; COVID-19; Mechanical ventilation; Pulse oximetry; Resource limited settings; SpO(2)/FiO(2).
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest None.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. 2021. https://covid19.who.int/ accessed 1 November 2021.
-
- Ranieri V.M., Rubenfeld G.D., Thompson B.T., Ferguson N.D., Caldwell E., Fan E., et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin definition. JAMA. 2012;307(23):2526–2533. - PubMed
-
- Villar J., Fernandez R.L., Ambros A., Parra L., Blanco J., Dominguez-Berrot A.M., et al. A clinical classification of the acute respiratory distress syndrome for predicting outcome and guiding medical therapy*. Crit Care Med. 2015;43(2):346–353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

