The regulation of KSHV lytic reactivation by viral and cellular factors
- PMID: 34872030
- PMCID: PMC8844089
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coviro.2021.11.004
The regulation of KSHV lytic reactivation by viral and cellular factors
Abstract
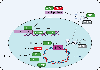
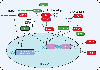
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is an oncogenic herpesvirus that exhibits two distinct phases of infection in the host-latent and lytic. The quiescent latent phase is defined by limited expression of a subset of viral proteins and microRNAs, and an absence of virus production. KSHV periodically reactivates from latency to undergo active lytic replication, leading to production of new infectious virions. This switch from the latent to the lytic phase requires the viral protein regulator of transcription activator (RTA). RTA, along with other virally encoded proteins, is aided by host factors to facilitate this transition. Herein, we highlight the key host proteins that are involved in mediating RTA activation and KSHV lytic replication and discuss the cellular processes in which they function. We will also focus on the modulation of viral reactivation by the innate immune system, and how KSHV influences key immune signaling pathways to aid its own lifecycle.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Activation of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) by inhibitors of class III histone deacetylases: identification of sirtuin 1 as a regulator of the KSHV life cycle.J Virol. 2014 Jun;88(11):6355-67. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00219-14. Epub 2014 Mar 26. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24672028 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and Subcellular Localization of the Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus K15P Protein during Latency and Lytic Reactivation in Primary Effusion Lymphoma Cells.J Virol. 2017 Oct 13;91(21):e01370-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01370-17. Print 2017 Nov 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28835496 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of Direct RTA Targets Reveals Key Host Factors for Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Lytic Reactivation.J Virol. 2019 Feb 19;93(5):e01978-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01978-18. Print 2019 Mar 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30541837 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of KSHV Latency and Lytic Reactivation.Viruses. 2020 Sep 17;12(9):1034. doi: 10.3390/v12091034. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32957532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular biology of KSHV lytic reactivation.Viruses. 2015 Jan 14;7(1):116-53. doi: 10.3390/v7010116. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 25594835 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A State-of-the-Art Review on the Recent Advances in Exosomes in Oncogenic Virus.Health Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 18;7(11):e70196. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70196. eCollection 2024 Nov. Health Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39558933 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Role of the Epstein-Barr Virus Encoded Deubiquitinating Enzyme (BPLF1) in mTOR-Mediated Cell Growth and Proliferation Pathways.Viruses. 2025 Aug 20;17(8):1139. doi: 10.3390/v17081139. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40872852 Free PMC article.
-
Design, development, and evaluation of gene therapeutics specific to KSHV-associated diseases.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 19:2025.02.19.639178. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.19.639178. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40027700 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Heat shock factor 2 regulates oncogenic gamma-herpesvirus gene expression by remodeling the chromatin at the ORF50 and BZLF1 promoter.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Apr 17;21(4):e1013108. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1013108. eCollection 2025 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40245053 Free PMC article.
-
miR-769-3p inhibits cellular proliferation of KSHV-infected SH-SY5Y cells through targeting mTOR.J Cancer. 2024 Apr 23;15(11):3338-3349. doi: 10.7150/jca.93595. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38817860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ballestas ME, Chatis PA, Kaye KM: Efficient persistence of extrachromosomal KSHV DNA mediated by latency-associated nuclear antigen. Science 1999, 284:641–644. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

