Assessment of foot-and-mouth disease risk areas in mainland China based spatial multi-criteria decision analysis
- PMID: 34872574
- PMCID: PMC8647368
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-021-03084-5
Assessment of foot-and-mouth disease risk areas in mainland China based spatial multi-criteria decision analysis
Abstract
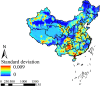
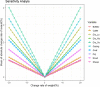
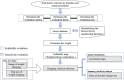
Background: Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) is a highly contagious viral disease of cloven-hoofed animals. As a transboundary animal disease, the prevention and control of FMD are important. This study was based on spatial multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) to assess FMD risk areas in mainland China. Ten risk factors were identified for constructing risk maps by scoring, and the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) was used to calculate the criteria weights of all factors. Different risk factors had different units and attributes, and fuzzy membership was used to standardize the risk factors. The weighted linear combination (WLC) and one-at-a-time (OAT) were used to obtain risk and uncertainty maps as well as to perform sensitivity analysis.
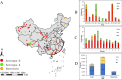
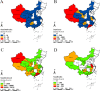
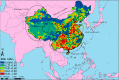
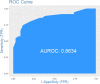
Results: Four major risk areas were identified in mainland China, including western (parts of Xinjiang and Tibet), southern (parts of Yunnan, Guizhou, Guangxi, Sichuan and Guangdong), northern (parts of Gansu, Ningxia and Inner Mongolia), and eastern (parts of Hebei, Henan, Anhui, Jiangsu and Shandong). Spring is the main season for FMD outbreaks. Risk areas were associated with the distance to previous outbreak points, grazing areas and cattle density. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis indicated that the risk map had good predictive power (AUC=0.8634).
Conclusions: These results can be used to delineate FMD risk areas in mainland China, and veterinary services can adopt the targeted preventive measures and control strategies.
Keywords: Analytic hierarchy process; Foot-and-mouth disease; Multi-criteria decision analysis; Risk areas.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of risk areas for foot and mouth disease in Thailand using a geographic information system-based multi-criteria decision analysis.Prev Vet Med. 2020 Dec;185:105183. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2020.105183. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Prev Vet Med. 2020. PMID: 33153767
-
Spatial risk assessment of foot and mouth disease in Sukabumi regency, Indonesia: A GIS and multicriteria decision analysis approach.Res Vet Sci. 2025 Aug;192:105694. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2025.105694. Epub 2025 May 14. Res Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40393338
-
Spatial distribution and risk areas of foot and mouth disease in mainland China.Prev Vet Med. 2021 Apr;189:105311. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2021.105311. Epub 2021 Feb 23. Prev Vet Med. 2021. PMID: 33652349
-
Epidemiological simulation modeling and spatial analysis for foot-and-mouth disease control strategies: a comprehensive review.Anim Health Res Rev. 2011 Dec;12(2):225-34. doi: 10.1017/S146625231100017X. Anim Health Res Rev. 2011. PMID: 22152294 Review.
-
Targeted FMD Vaccines for Eastern Africa: The AgResults Foot and Mouth Disease Vaccine Challenge Project.Viruses. 2021 Sep 14;13(9):1830. doi: 10.3390/v13091830. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34578411 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A scoping review of foot-and-mouth disease risk, based on spatial and spatio-temporal analysis of outbreaks in endemic settings.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2022 Nov;69(6):3198-3215. doi: 10.1111/tbed.14769. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2022. PMID: 36383164 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology and economics of foot-and-mouth disease: current understanding and knowledge gaps.Vet Res. 2025 Jul 7;56(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s13567-025-01561-5. Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40624570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and application of a WebGIS-based prediction system for multi-criteria decision analysis of porcine pasteurellosis.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 10;14(1):21082. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72350-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39256567 Free PMC article.
-
Ecological niche modeling for surveillance of foot-and-mouth disease in South Asia.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 22;20(4):e0320921. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320921. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40261938 Free PMC article.
-
A review of foot-and-mouth disease in Ethiopia: epidemiological aspects, economic implications, and control strategies.Virol J. 2023 Dec 15;20(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-02263-0. Virol J. 2023. PMID: 38102688 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations . Foot-and-mouth disease frequently asked questions. 2012.
-
- OIE . World Animal Health Information Database (WAHIS) Interface. 2020.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

