Stress Signal ULBP4, an NKG2D Ligand, Is Upregulated in Multiple Sclerosis and Shapes CD8+ T-Cell Behaviors
- PMID: 34873031
- PMCID: PMC8656234
- DOI: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000001119
Stress Signal ULBP4, an NKG2D Ligand, Is Upregulated in Multiple Sclerosis and Shapes CD8+ T-Cell Behaviors
Abstract
Background and objectives: We posit the involvement of the natural killer group 2D (NKG2D) pathway in multiple sclerosis (MS) pathology via the presence of specific NKG2D ligands (NKG2DLs). We aim to evaluate the expression of NKG2DLs in the CNS and CSF of patients with MS and to identify cellular stressors inducing the expression of UL16-binding protein 4 (ULBP4), the only detectable NKG2DL. Finally, we evaluate the impact of ULBP4 on functions such as cytokine production and motility by CD8+ T lymphocytes, a subset largely expressing NKG2D, the cognate receptor.
Methods: Human postmortem brain samples and CSF from patients with MS and controls were used to evaluate NKG2DL expression. In vitro assays using primary cultures of human astrocytes and neurons were performed to identify stressors inducing ULBP4 expression. Human CD8+ T lymphocytes from MS donors and age/sex-matched healthy controls were isolated to evaluate the functional impact of soluble ULBP4.
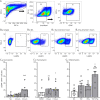
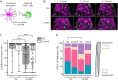
Results: We detected mRNA coding for the 8 identified human NKG2DLs in brain samples from patients with MS and controls, but only ULBP4 protein expression was detectable by Western blot. ULBP4 levels were greater in patients with MS, particularly in active and chronic active lesions and normal-appearing white matter, compared with normal-appearing gray matter from MS donors and white and gray matter from controls. Soluble ULBP4 was also detected in CSF of patients with MS and controls, but a smaller shed/soluble form of 25 kDa was significantly elevated in CSF from female patients with MS compared with controls and male patients with MS. Our data indicate that soluble ULBP4 affects various functions of CD8+ T lymphocytes. First, it enhanced the production of the proinflammatory cytokines GM-CSF and interferon-γ (IFNγ). Second, it increased CD8+ T lymphocyte motility and favored a kinapse-like behavior when cultured in the presence of human astrocytes. CD8+ T lymphocytes from patients with MS were especially altered by the presence of soluble ULBP4 compared with healthy controls.
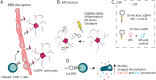
Discussion: Our study provides new evidence for the involvement of NKG2D and its ligand ULBP4 in MS pathology. Our results point to ULBP4 as a viable target to specifically block 1 component of the NKG2D pathway without altering immune surveillance involving other NKG2DL.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The NKG2D ligand ULBP4 binds to TCRgamma9/delta2 and induces cytotoxicity to tumor cells through both TCRgammadelta and NKG2D.Blood. 2009 Jul 9;114(2):310-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-12-196287. Epub 2009 May 12. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19436053
-
Cutting an NKG2D Ligand Short: Cellular Processing of the Peculiar Human NKG2D Ligand ULBP4.Front Immunol. 2018 Mar 29;9:620. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00620. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29651291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Four novel ULBP splice variants are ligands for human NKG2D.Int Immunol. 2008 Aug;20(8):981-91. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxn057. Epub 2008 Jun 10. Int Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18544572
-
Specific alterations in NKG2D+ T lymphocytes in relapsing-remitting and progressive multiple sclerosis patients.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2023 Mar;71:104542. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2023.104542. Epub 2023 Jan 26. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2023. PMID: 36716577
-
Release of Soluble Ligands for the Activating NKG2D Receptor: One More Immune Evasion Strategy Evolved by HIV-1 ?Curr Drug Targets. 2016;17(1):54-64. doi: 10.2174/1389450116666150630110329. Curr Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 26122035 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of NKG2D and Its Ligands in Autoimmune Diseases: New Targets for Immunotherapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 16;24(24):17545. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417545. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Classification of T lymphocyte motility behaviors using a machine learning approach.PLoS Comput Biol. 2023 Sep 11;19(9):e1011449. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011449. eCollection 2023 Sep. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023. PMID: 37695797 Free PMC article.
-
The current state of knowledge on the role of NKG2D ligands in multiple sclerosis and other autoimmune diseases.Front Mol Neurosci. 2025 Jan 10;17:1493308. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1493308. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39866909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of selected NKG2DLs such as MICA, MICB and ULBP4 as potential markers in multiple sclerosis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 29;15(1):27562. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12589-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40730869 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytes and Inflammatory T Helper Cells: A Dangerous Liaison in Multiple Sclerosis.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 8;13:824411. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.824411. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35211120 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
