Matrix stiffness modulates hepatic stellate cell activation into tumor-promoting myofibroblasts via E2F3-dependent signaling and regulates malignant progression
- PMID: 34873170
- PMCID: PMC8648844
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-021-04418-9
Matrix stiffness modulates hepatic stellate cell activation into tumor-promoting myofibroblasts via E2F3-dependent signaling and regulates malignant progression
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Matrix stiffness modulates hepatic stellate cell activation into tumor-promoting myofibroblasts via E2F3-dependent signaling and regulates malignant progression.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Jan 28;13(1):91. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04528-y. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35091557 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
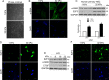
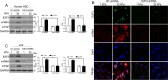
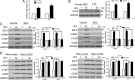
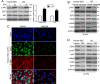
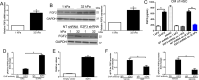
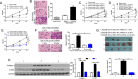
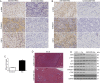
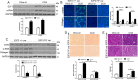
The hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) activation by myofibroblastic differentiation is critical for liver fibrosis. Crosstalk between stromal cells and tumor cells in the microenvironment alters the properties and facilitates the growth and metastasis of tumor cells. How mechanical stimuli originally stiffness of extracellular matrix (ECM) contribute to tumor development remains poorly understood. Here, we demonstrated that stiffness contributes to mechanosignal transduction in HSCs, which promotes hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells growth and metastasis through secretion of FGF2. On stiffness matrix, HSCs activation was confirmed by immunofluorescence (IF) and Western blot (WB) for α-smooth muscle actin (SMA). Increasing matrix stiffness promoted HSCs activation by CD36-AKT-E2F3 mechanosignaling through shRNA-mediated E2F3 knockdown, AKT inhibitors, and CD36 shRNA. Moreover, ChIP-qPCR. Confirmed that E2F3 combined the promoter of FGF2, and stiffness promoted FGF2 expression. On a stiff matrix, HCC cells cultured with conditioned media (CM) from HSCs increased HCC cells growth and metastasis by binding FGFR1 to activate PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK signaling pathways. Moreover, conditional E2F3 knockout mice were subjected to CCl4 treatment to assess the role of E2F3 in HSC activation. Additionally, the DEN-induced HCC model was also used to evaluate the role of E2F3 in liver fibrosis and HCC growth. In conclusion, we demonstrated that stiffness-induced HSC activation by E2F3 dependent. Stiffness activated CD36-AKT-E2F3 signaling and targeted FGF2 transcription, subsequently, activated HCC growth and metastasis by FGFR1-mediated PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK signaling.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
P300 Acetyltransferase Mediates Stiffness-Induced Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells Into Tumor-Promoting Myofibroblasts.Gastroenterology. 2018 Jun;154(8):2209-2221.e14. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.02.015. Epub 2018 Feb 15. Gastroenterology. 2018. PMID: 29454793 Free PMC article.
-
HSCs-derived COMP drives hepatocellular carcinoma progression by activating MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Sep 19;37(1):231. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0908-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30231922 Free PMC article.
-
KGF secreted from HSCs activates PAK4/BMI1, promotes HCC stemness through PI3K/AKT pathway.IUBMB Life. 2025 Jan;77(1):e2929. doi: 10.1002/iub.2929. Epub 2024 Nov 15. IUBMB Life. 2025. PMID: 39544166
-
Deciphering the possible reciprocal loop between hepatic stellate cells and cancer cells in the tumor microenvironment of the liver.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2023 Feb;182:103902. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2022.103902. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2023. PMID: 36621514 Review.
-
Hepatic stellate cells and extracellular matrix in hepatocellular carcinoma: more complicated than ever.Liver Int. 2014 Jul;34(6):834-43. doi: 10.1111/liv.12465. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Liver Int. 2014. PMID: 24397349 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of CFHR4 as a Potential Prognosis Biomarker Associated With lmmune Infiltrates in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 22;13:892750. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.892750. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35812416 Free PMC article.
-
Forcing the code: tension modulates signaling to drive morphogenesis and malignancy.Genes Dev. 2025 Jan 7;39(1-2):163-181. doi: 10.1101/gad.352110.124. Genes Dev. 2025. PMID: 39638568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid Nanoparticles-Based Therapy in Liver Metastasis Management: From Tumor Cell-Directed Strategy to Liver Microenvironment-Directed Strategy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Jun 2;18:2939-2954. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S402821. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37288351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of DNMT3B expression in activated hepatic stellate cells overcomes chemoresistance in the tumor microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 2;14(1):115. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50680-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38168140 Free PMC article.
-
Redox signaling-mediated tumor extracellular matrix remodeling: pleiotropic regulatory mechanisms.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024 Apr;47(2):429-445. doi: 10.1007/s13402-023-00884-9. Epub 2023 Oct 4. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024. PMID: 37792154 Review.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA: Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

