Systems biology and machine learning approaches identify drug targets in diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 34873190
- PMCID: PMC8648918
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-02282-3
Systems biology and machine learning approaches identify drug targets in diabetic nephropathy
Abstract
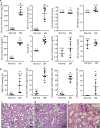
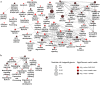
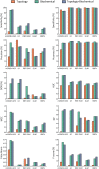
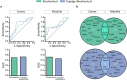
Diabetic nephropathy (DN), the leading cause of end-stage renal disease, has become a massive global health burden. Despite considerable efforts, the underlying mechanisms have not yet been comprehensively understood. In this study, a systematic approach was utilized to identify the microRNA signature in DN and to introduce novel drug targets (DTs) in DN. Using microarray profiling followed by qPCR confirmation, 13 and 6 differentially expressed (DE) microRNAs were identified in the kidney cortex and medulla, respectively. The microRNA-target interaction networks for each anatomical compartment were constructed and central nodes were identified. Moreover, enrichment analysis was performed to identify key signaling pathways. To develop a strategy for DT prediction, the human proteome was annotated with 65 biochemical characteristics and 23 network topology parameters. Furthermore, all proteins targeted by at least one FDA-approved drug were identified. Next, mGMDH-AFS, a high-performance machine learning algorithm capable of tolerating massive imbalanced size of the classes, was developed to classify DT and non-DT proteins. The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and precision of the proposed method were 90%, 86%, 88%, and 89%, respectively. Moreover, it significantly outperformed the state-of-the-art (P-value ≤ 0.05) and showed very good diagnostic accuracy and high agreement between predicted and observed class labels. The cortex and medulla networks were then analyzed with this validated machine to identify potential DTs. Among the high-rank DT candidates are Egfr, Prkce, clic5, Kit, and Agtr1a which is a current well-known target in DN. In conclusion, a combination of experimental and computational approaches was exploited to provide a holistic insight into the disorder for introducing novel therapeutic targets.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comprehensive analysis of diabetic nephropathy expression profile based on weighted gene co-expression network analysis algorithm.BMC Nephrol. 2021 Jul 2;22(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02447-2. BMC Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 34215202 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of miRNAs-genes regulatory network in diabetic nephropathy based on bioinformatics analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Jul;98(27):e16225. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016225. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31277135 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic expression profiling and bioinformatics analysis on diabetic nephrology with ginsenoside Rg3.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Aug;14(2):1162-72. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5349. Epub 2016 May 27. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27279428 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of candidate microRNA biomarkers in diabetic nephropathy: a meta-analysis of profiling studies.J Nephrol. 2018 Dec;31(6):813-831. doi: 10.1007/s40620-018-0511-5. Epub 2018 Jul 17. J Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 30019103 Review.
-
Network pharmacology-based identification of miRNA expression of Astragalus membranaceus in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Feb 4;101(5):e28747. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028747. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35119030 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Network-based identification and prioritization of key transcriptional factors of diabetic kidney disease.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Jan 2;21:716-730. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.12.054. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 36659918 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Scoring Function Space: Developing Computational Models for Drug Discovery.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(17):2361-2377. doi: 10.2174/0929867330666230321103731. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 36944627 Review.
-
miR-802-5p is a key regulator in diabetic kidney disease.J Res Med Sci. 2023 May 29;28:43. doi: 10.4103/jrms.jrms_702_22. eCollection 2023. J Res Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37405075 Free PMC article.
-
From bytes to nephrons: AI's journey in diabetic kidney disease.J Nephrol. 2025 Jan;38(1):25-35. doi: 10.1007/s40620-024-02050-2. Epub 2024 Aug 12. J Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39133462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of miR-802 in Diabetic Kidney Disease: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Insights.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 7;26(12):5474. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125474. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40564936 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pranavkrishna S, Sanjeev G, Akshaya RL, Rohini M, Selvamurugan N. A computational approach on studying the regulation of TGF-β1-stimulated Runx2 expression by MicroRNAs in human breast cancer cells. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021;137:104823. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

