Pulmonary Diffuse Airspace Opacities Diagnosis from Chest X-Ray Images Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Fine-Tuned by Whale Optimizer
- PMID: 34873379
- PMCID: PMC8635480
- DOI: 10.1007/s11277-021-09410-2
Pulmonary Diffuse Airspace Opacities Diagnosis from Chest X-Ray Images Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Fine-Tuned by Whale Optimizer
Abstract
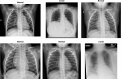
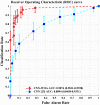
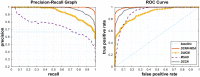
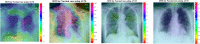
The early diagnosis and the accurate separation of COVID-19 from non-COVID-19 cases based on pulmonary diffuse airspace opacities is one of the challenges facing researchers. Recently, researchers try to exploit the Deep Learning (DL) method's capability to assist clinicians and radiologists in diagnosing positive COVID-19 cases from chest X-ray images. In this approach, DL models, especially Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (DCNN), propose real-time, automated effective models to detect COVID-19 cases. However, conventional DCNNs usually use Gradient Descent-based approaches for training fully connected layers. Although GD-based Training (GBT) methods are easy to implement and fast in the process, they demand numerous manual parameter tuning to make them optimal. Besides, the GBT's procedure is inherently sequential, thereby parallelizing them with Graphics Processing Units is very difficult. Therefore, for the sake of having a real-time COVID-19 detector with parallel implementation capability, this paper proposes the use of the Whale Optimization Algorithm for training fully connected layers. The designed detector is then benchmarked on a verified dataset called COVID-Xray-5k, and the results are verified by a comparative study with classic DCNN, DUICM, and Matched Subspace classifier with Adaptive Dictionaries. The results show that the proposed model with an average accuracy of 99.06% provides 1.87% better performance than the best comparison model. The paper also considers the concept of Class Activation Map to detect the regions potentially infected by the virus. This was found to correlate with clinical results, as confirmed by experts. Although results are auspicious, further investigation is needed on a larger dataset of COVID-19 images to have a more comprehensive evaluation of accuracy rates.
Keywords: COVID-19; Chest X-rays; Deep convolutional neural networks; Whale optimization algorithm.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures






References
-
- Abdel-Basset M, Mohamed R, Elhoseny M, Chakrabortty RK, Ryan M. A hybrid COVID-19 detection model using an improved marine predators algorithm and a ranking-based diversity reduction strategy. IEEE Access. 2020;8:79521–79540. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2990893. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
