Low intratumoral genetic neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is associated with favorable tumor immune microenvironment and with survival in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC)
- PMID: 34873491
- PMCID: PMC8640806
Low intratumoral genetic neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is associated with favorable tumor immune microenvironment and with survival in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC)
Abstract
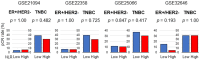
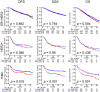
Patients with triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) have a poor prognosis. A novel prognostic biomarker may guide management by appropriately selecting patients for particular treatments. Peripheral blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) was reported to associate with cancer progression, thus we hypothesized that intratumor genetic NLR will reflect tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) and breast cancer biology. The intratumoral genetic NLR previously defined as the ratio of CD66b (CEACAM8) and CD8 (CD8A) gene expressions was utilized to analyze total of 2,994 patients from METABRIC, TCGA, GSE21094, GSE22358, GSE25088, GSE32646, and GSE2603 cohorts. Intratumoral genetic NLR did not correlate with cancer stage nor clinical parameters of cancer cell proliferation such as Nottingham histological grade or MKI67 expression levels in neither the METABRIC or TCGA cohorts. Intratumoral genetic NLR-high breast cancer was not associated with pathologic complete response (pCR) after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in 5 independent cohorts with different regimens. Despite these results, intratumoral genetic NLR-high TNBC demonstrated worse disease-free, disease-specific, and overall survival. Intratumoral genetic NLR-low TNBC enriched multiple immune-related gene sets, was associated with higher favorable immune-related scores and with a favorable TIME, whereas no gene sets enriched to NLR-high TNBC. In conclusion, intratumoral genetic NLR-low TNBC was associated with favorable TIME and with better survival.
Keywords: GSEA; NLR; Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; TNBC; breast cancer; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; triple negative breast cancer; tumor immune microenvironment; xCell.
AJCR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




References
-
- Waks AG, Winer EP. Breast cancer treatment: a review. JAMA. 2019;321:288–300. - PubMed
-
- Katsuta E, Rashid OM, Takabe K. Clinical relevance of tumor microenvironment: immune cells, vessels, and mouse models. Hum Cell. 2020;33:930–937. - PubMed
-
- Hajizadeh F, Aghebati Maleki L, Alexander M, Mikhailova MV, Masjedi A, Ahmadpour M, Hashemi V, Jadidi-Niaragh F. Tumor-associated neutrophils as new players in immunosuppressive process of the tumor microenvironment in breast cancer. Life Sci. 2021;264:118699. - PubMed
-
- Gregory AD, Houghton AM. Tumor-associated neutrophils: new targets for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2011;71:2411–2416. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
